Genetic mechanisms underlying tumor microenvironment composition and function in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 38211334
- PMCID: PMC10972714
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2023021002
Genetic mechanisms underlying tumor microenvironment composition and function in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
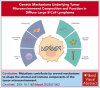
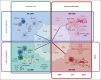
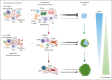
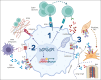
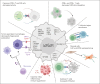
Cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) show enormous diversity and plasticity, with functions that can range from tumor inhibitory to tumor supportive. The patient's age, immune status, and DLBCL treatments are factors that contribute to the shaping of this TME, but evidence suggests that genetic factors, arising principally in lymphoma cells themselves, are among the most important. Here, we review the current understanding of the role of these genetic drivers of DLBCL in establishing and modulating the lymphoma microenvironment. A better comprehension of the relationship between lymphoma genetic factors and TME biology should lead to better therapeutic interventions, especially immunotherapies.
© 2024 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Introduction to a review series on the influence of the tumor microenvironment on the pathogenesis of B-cell lymphomas.Blood. 2024 Mar 21;143(12):1057-1058. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023021003. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38512261 No abstract available.
References
-
- Frontzek F, Lenz G. Novel insights into the pathogenesis of molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and their clinical implications. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019;12(11):1059–1067. - PubMed
-
- Gerber-Ferder Y, Cosgrove J, Duperray-Susini A, et al. Breast cancer remotely imposes a myeloid bias on haematopoietic stem cells by reprogramming the bone marrow niche. Nat Cell Biol. 2023;25(12):1736–1745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

