The influence of zwitterionic and anionic phospholipids on protein aggregation
- PMID: 38211368
- PMCID: PMC12137201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2024.107174
The influence of zwitterionic and anionic phospholipids on protein aggregation
Abstract
The progressive aggregation of misfolded proteins is the underlying molecular cause of numerous pathologies including Parkinson's disease and injection and transthyretin amyloidosis. A growing body of evidence indicates that protein deposits detected in organs and tissues of patients diagnosed with such pathologies contain fragments of lipid membranes. In vitro experiments also showed that lipid membranes could strongly change the aggregation rate of amyloidogenic proteins, as well as alter the secondary structure and toxicity of oligomers and fibrils formed in their presence. In this review, the effect of large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs) composed of zwitterionic and anionic phospholipids on the aggregation rate of insulin, lysozyme, transthyretin (TTR) and α- synuclein (α-syn) will be discussed. The manuscript will also critically review the most recent findings on the lipid-induced changes in the secondary structure of protein oligomers and fibrils, as well as reveal the extent to which lipids could alter the toxicity of protein aggregates formed in their presence.
Keywords: Amyloid fibrils; LUVs; Neurodegeneration; Oligomers; Toxicity.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Dmitry Kurouski reports financial support was provided by Texas A&M University. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


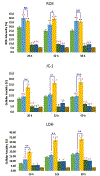
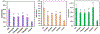
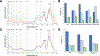

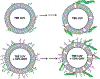
References
-
- Eisenberg DS, Sawaya MR, Structural studies of amyloid proteins at the molecular level, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 86 (2017) 69–95. - PubMed
-
- Nelson R, Eisenberg D, Structural models of amyloid-like fibrils, Adv. Protein Chem. 73 (2006) 235–282. - PubMed
-
- Chen SW, Drakulic S, Deas E, Ouberai M, Aprile FA, Arranz R, Ness S, Roodveldt C, Guilliams T, De-Genst EJ, Klenerman D, Wood NW, Knowles TP, Alfonso C, Rivas G, Abramov AY, Valpuesta JM, Dobson CM, Cremades N, Structural characterization of toxic oligomers that are kinetically trapped during alpha-synuclein fibril formation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 (2015) E1994–E2003. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiti F, Dobson CM, Protein Misfolding, amyloid formation, and human disease: a summary of Progress over the last decade, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 86 (2017) 27–68. - PubMed
-
- Knowles TP, Vendruscolo M, Dobson CM, The amyloid state and its association with protein misfolding diseases, Nat. Rev. 15 (2014) 384–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

