Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Kidney Disease: Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analyses
- PMID: 38211557
- PMCID: PMC10958583
- DOI: 10.2337/db23-0564
Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Kidney Disease: Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analyses
Abstract
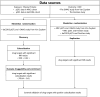
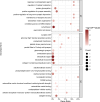
At present, safe and effective treatment drugs are urgently needed for diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Circulating protein biomarkers with causal genetic evidence represent promising drug targets, which provides an opportunity to identify new therapeutic targets. Summary data from two protein quantitative trait loci studies are presented, one involving 4,907 plasma proteins data from 35,559 individuals and the other encompassing 4,657 plasma proteins among 7,213 European Americans. Summary statistics for DKD were obtained from a large genome-wide association study (3,345 cases and 2,372 controls) and the FinnGen study (3,676 cases and 283,456 controls). Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was conducted to examine the potential targets for DKD. The colocalization analysis was used to detect whether the potential proteins exist in the shared causal variants. To enhance the credibility of the results, external validation was conducted. Additionally, enrichment analysis, assessment of protein druggability, and the protein-protein interaction networks were used to further enrich the research findings. The proteome-wide MR analyses identified 21 blood proteins that may causally be associated with DKD. Colocalization analysis further supported a causal relationship between 12 proteins and DKD, with external validation confirming 4 of these proteins, and TGFBI was affirmed through two separate group data sets. These results indicate that targeting these four proteins could be a promising approach for treating DKD, and warrant further clinical investigations.
© 2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteome-wide Mendelian randomization reveals causal associations between plasma proteins and autoimmune thyroid disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 6;15(1):19898. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04902-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40481092 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Potential Drug Targets in Multiple Cardiovascular Diseases: A Study Based on Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analysis.Cardiovasc Ther. 2025 Feb 21;2025:5711316. doi: 10.1155/cdr/5711316. eCollection 2025. Cardiovasc Ther. 2025. PMID: 40026415 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization Identifies Therapeutic Targets for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Feb 4;14(3):e038193. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.038193. Epub 2025 Feb 3. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 39895541 Free PMC article.
-
Role of circulating inflammatory protein in the development of diabetic renal complications: proteome-wide Mendelian randomization and colocalization analyses.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 8;15:1406442. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1406442. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39040677 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the genetic relationship between ulcerative colitis and diabetic kidney disease: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 15;15:1435812. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1435812. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39211444 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mendelian randomization analysis reveals causal factors behind diabetic nephropathy: evidence, opportunities, and challenges.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 13;15:1444808. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1444808. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39735650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targets for Sepsis: Multicenter Proteome-Wide Analyses and Experimental Validation.J Proteome Res. 2025 Jul 4;24(7):3498-3506. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5c00148. Epub 2025 Jun 3. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40459852 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targets for age-related macular degeneration: proteome-wide Mendelian randomization and colocalization analyses.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 6;15:1400557. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1400557. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38903171 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-wide Mendelian randomization and colocalization analysis identify therapeutic targets for stroke.BMC Neurol. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04239-9. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40596960 Free PMC article.
-
The Omics-Driven Machine Learning Path to Cost-Effective Precision Medicine in Chronic Kidney Disease.Proteomics. 2025 Jun;25(11-12):e202400108. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202400108. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 39790049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, et al. ; FIDELIO-DKD Investigators . Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2020;383:2219–2229 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

