Low serum apolipoprotein A1 level predicts poor prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the real world: a retrospective study
- PMID: 38212711
- PMCID: PMC10785512
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-11818-5
Low serum apolipoprotein A1 level predicts poor prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the real world: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) is a member of the apolipoprotein family with diverse functions. It is associated with the pathogenesis and prognosis of several types of tumors. However, the role of serum apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) in the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) remains unclear. This study aimed to elucidate its influence on clinical outcomes in patients with DLBCL.
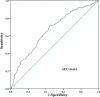
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed a cohort of 1583 consecutive DLBCL patients admitted to the Fujian Medical University Union Hospital between January 2011 and December 2021. 949 newly diagnosed DLBCL patients who met the inclusion criteria were enrolled for statistical analysis. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to determine the optimal cut-off value for serum ApoA1 levels for prognostic prediction among patients with DLBCL. The correlations between serum ApoA1 levels and clinical and laboratory parameters were analyzed. Prognostic significance was analyzed using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models.
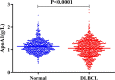
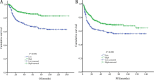
Results: Newly diagnosed patients with DLBCL demonstrated low serum ApoA1 levels (< 0.925 g/L), had more B symptoms, higher levels of serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (>upper limit of normal), poorer performance status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score of 2-4), higher percentage of advanced stage and non-germinal center B-cell (non-GCB) subtype, more cases of > 1 extranodal site, higher International Prognostic Index (IPI) score (3-5), and higher incidence of relapse or refractory diseases compared with those with high serum ApoA1 levels (≥ 0.925 g/L). Low serum ApoA1 levels were an independent adverse prognostic factor for overall survival (OS) but not progression-free survival (PFS).
Conclusions: Low serum ApoA1 levels were associated with poor treatment response and inferior survival in newly diagnosed patients with DLBCL.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein A1; DLBCL; Prognostic factor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U, Van Den Neste E, Kuruvilla J, Westin J, Link BK, Hay A, Cerhan JR, Zhu L, et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood. 2017;130(16):1800–1808. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-03-769620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Han Y, Yang J, Liu P, He X, Zhang C, Zhou S, Zhou L, Qin Y, Song Y, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on nodal or extranodal primary sites of origin: analysis of 1,085 WHO classified cases in a single institution in China. Chin J Cancer Res. 2019;31(1):152–161. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.01.10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

