Impact of baseline and trajectory of the atherogenic index of plasma on incident diabetic kidney disease and retinopathy in participants with type 2 diabetes: a longitudinal cohort study
- PMID: 38212770
- PMCID: PMC10782533
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02003-5
Impact of baseline and trajectory of the atherogenic index of plasma on incident diabetic kidney disease and retinopathy in participants with type 2 diabetes: a longitudinal cohort study
Abstract
Background: Some studies have assessed the predictive role of the atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) for macrovascular diseases. This prospective investigation aimed to elucidate whether AIP is associated with diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and diabetic retinopathy (DR) incidence.
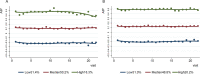
Methods: The data were extracted from 4831 participants, of whom 2943 and 3360 participants with type 2 diabetes (T2D) were included in the DKD and DR follow-up analyses, respectively. Cox regression models were performed to test the relationships of AIP value at baseline with the risk of incident DKD and DR. Group-based trajectory modelling was utilized to discern AIP trajectories during the follow-up period. Subsequently, logistic regressions were applied to ascertain the influence of AIP trajectories on the incidence of DKD and DR.
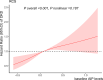
Results: During the follow-up period, 709 (24.1%) and 193 (5.7%) participants developed DKD and DR, respectively. The median (interquartile range) follow-up time was 24.2 (26.3) months for DKD and 25.7 (27.0) months for DR. According to the multivariate Cox regression models, baseline AIP was positively and linearly related to the occurrence of DKD, with a hazard ratio of 1.75 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.36-2.26). Three distinct trajectories of AIP were identified throughout the follow-up time: Low (31.4%), Median (50.2%), and High (18.3%). Compared to participants with the Low AIP trajectory, those with High and Median AIP trajectories presented 117% (95% CI: 1.62-2.91) and 84% (95% CI 1.46-2.32) greater odds of developing DKD, respectively. However, neither baseline levels nor trajectories of AIP were shown to be related to DR after adjusting for confounding factors.
Conclusions: Baseline levels and trajectories of AIP were independently related to elevated DKD risk, indicating that AIP could be used as a predictor for identifying T2D participants at higher risk of DKD. No association between AIP and DR was detected.
Keywords: Atherogenic index of plasma; Diabetic kidney disease; Diabetic retinopathy; Lipid profile; Trajectory; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of baseline and trajectory of the cardiometabolic indices on incident microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes.Atherosclerosis. 2025 Aug;407:120407. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2025.120407. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Atherosclerosis. 2025. PMID: 40561674
-
Association between atherogenic index of plasma and type 2 diabetic complications: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 4;16:1537303. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1537303. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39968299 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a risk prediction model for diabetic kidney disease in patients with diabetic retinopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 5;16:1499866. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1499866. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40391008 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors for the development and progression of proliferative diabetic retinopathy in people with diabetic retinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 22;2(2):CD013775. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013775.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36815723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Early Diabetic Kidney Disease Based on a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 20 Cohorts.Diabetes Care. 2020 Apr;43(4):925-933. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1897. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 32198286
Cited by
-
Associations of combined lifestyle and metabolic risks with cancer incidence in the UK biobank study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 26;25(1):547. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13955-x. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40140964 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Lipid Parameters on Visual Acuity Change in Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Dec 16;18:3791-3800. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S500368. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39712368 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline atherogenic index of plasma and its trajectory predict onset of type 2 diabetes in a health screened adult population: a large longitudinal study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Feb 7;24(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02619-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39920728 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Lipid Biomarkers and Microvascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2025 Aug 16;18:11795514251365301. doi: 10.1177/11795514251365301. eCollection 2025. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40827201 Free PMC article.
-
Association of atherogenic index of plasma trajectory with the incidence of cardiovascular disease over a 12-year follow-up: findings from the ELSA cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 19;24(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02677-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40108582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- no. DMRFP_II_05/the Shanghai Medical and Health Development Foundation
- no. DMRFP_II_01/the Shanghai Medical and Health Development Foundation
- no. Z155080000004/the Capacity building for multidisciplinary cooperation in diagnosis and treatment of major metabolic diseases
- no. 82270896/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

