Lipoxins A4 and B4 inhibit glial cell activation via CXCR3 signaling in acute retinal neuroinflammation
- PMID: 38212822
- PMCID: PMC10782675
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-024-03010-0
Lipoxins A4 and B4 inhibit glial cell activation via CXCR3 signaling in acute retinal neuroinflammation
Abstract
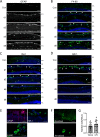
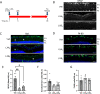
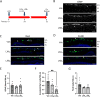
Lipoxins are small lipids that are potent endogenous mediators of systemic inflammation resolution in a variety of diseases. We previously reported that Lipoxins A4 and B4 (LXA4 and LXB4) have protective activities against neurodegenerative injury. Yet, lipoxin activities and downstream signaling in neuroinflammatory processes are not well understood. Here, we utilized a model of posterior uveitis induced by lipopolysaccharide endotoxin (LPS), which results in rapid retinal neuroinflammation primarily characterized by activation of resident macroglia (astrocytes and Müller glia), and microglia. Using this model, we observed that each lipoxin reduces acute inner retinal inflammation by affecting endogenous glial responses in a cascading sequence beginning with astrocytes and then microglia, depending on the timing of exposure; prophylactic or therapeutic. Subsequent analyses of retinal cytokines and chemokines revealed inhibition of both CXCL9 (MIG) and CXCL10 (IP10) by each lipoxin, compared to controls, following LPS injection. CXCL9 and CXCL10 are common ligands for the CXCR3 chemokine receptor, which is prominently expressed in inner retinal astrocytes and ganglion cells. We found that CXCR3 inhibition reduces LPS-induced neuroinflammation, while CXCR3 agonism alone induces astrocyte reactivity. Together, these data uncover a novel lipoxin-CXCR3 pathway to promote distinct anti-inflammatory and proresolution cascades in endogenous retinal glia.
Keywords: CXCL10; CXCL9; CXCR3; Gliosis; Inflammation resolution; Lipoxins; Neuroinflammation; Retina; Uveitis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Several authors (I. L-B, J.M.S., K.G.) have obtained a US patent for use of lipoxins to treat neurodegeneration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Astrocyte-derived lipoxins A4 and B4 promote neuroprotection from acute and chronic injury.J Clin Invest. 2017 Dec 1;127(12):4403-4414. doi: 10.1172/JCI77398. Epub 2017 Nov 6. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 29106385 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Lipoxin A4 and B4 Signaling on the Inner Retina in a Mouse Model of Experimental Glaucoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 19:2024.01.17.575414. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.17.575414. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38293224 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Regulation of disease-associated microglia in the optic nerve by lipoxin B4 and ocular hypertension.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Nov 20;19(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00775-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39568070 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxin and synthetic lipoxin analogs: an overview of anti-inflammatory functions and new concepts in immunomodulation.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006 Apr;5(2):91-106. doi: 10.2174/187152806776383125. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16613568 Review.
-
Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxins are the first lipid mediators of endogenous anti-inflammation and resolution.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005 Sep-Oct;73(3-4):141-62. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2005.05.002. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005. PMID: 16005201 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipidomic Analysis Reveals Drug-Induced Lipoxins in Glaucoma Treatment.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 27:2025.01.24.634771. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.24.634771. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975338 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Retinal cytoarchitecture is preserved in an organotypic perfused human and porcine eye model.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Nov 30;12(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01892-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 39616406 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) as a Potential Drug for Diabetic Retinopathy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 21;61(2):177. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020177. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40005295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

