Comparative Histological Study of Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells versus Mesenchymal Stem Cells Co-Cultured with Liver Tissue on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Adult Male Albino Rats
- PMID: 38213650
- PMCID: PMC10779448
- DOI: 10.4103/jmau.jmau_62_21
Comparative Histological Study of Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells versus Mesenchymal Stem Cells Co-Cultured with Liver Tissue on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Adult Male Albino Rats
Abstract
Context: Liver diseases are major causes of morbidity and mortality. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic effects, so they can be used in the treatment of liver diseases. MSCs co-cultured with diseased liver tissue improve the homing capacity, survival rate, and paracrine effects of the MSCs, as well as the ability to enhance liver function.
Aims: This work aimed to study the therapeutic effect of MSCs versus MSCs co-cultured with liver tissue on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatotoxicity in adult male albino rats.
Settings and design: Twenty adult male albino rats were divided into four equal groups; Group I (control group), Group II received CCl4 intraperitoneally (i.p.), Group III received CCl4 i.p. and then injected with MSCs intravenously (i.v.), and Group IV received CCl4 i.p. and then injected with co-cultured MSCs i.v.
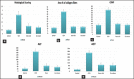
Materials and methods: Finally, liver specimens were processed for light microscopy (LM) and electron microscopy (EM). Statistical analysis was carried out to assess histological scoring, area percentage of collagen fibers, number of glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive cells, and biochemical analysis of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase.
Statistical analysis used: Statistical analysis of (histological scoring, area % of collagen fibers, and biochemical analysis) was done by using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test using graphpad software (SanDiego, CA, USA). The means ± standard deviations were used for statistical analysis.
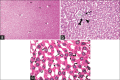
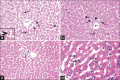
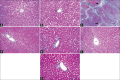
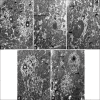
Results: LM of Group II revealed loss of hepatic architecture and diffuse fibrosis with dilated congested blood vessels, bile ductular proliferation, and cellular infiltrations. Vacuolated cytoplasm with or without pyknotic nuclei was observed in addition to micro- and macro-steatosis. EM demonstrated disfigured hepatocytes with abnormal organelles surrounding atypical nucleus. Group III showed restoration of the normal liver architecture with greater extent in Group IV. Statistical analysis confirmed the microscopic findings.
Conclusions: Co-cultured MSCs with diseased liver tissue augmented the therapeutic effects of MSCs in treating hepatotoxicity induced by CCl4 in adult male albino rats.
Keywords: Carbon tetrachloride; co-cultured mesenchymal stem cells; hepatotoxicity; mesenchymal stem cells.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison between the Regenerative and Therapeutic Impacts of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Pre-Treated with Melatonin on Liver Fibrosis.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 1;14(3):297. doi: 10.3390/biom14030297. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540717 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte-like Versus Mesenchymal Stem Cells in CCl4-induced Liver Fibrosis.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017 Nov/Dec;25(10):736-745. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000373. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017. PMID: 27153445
-
Mesenchymal stem cells: In vivo therapeutic application ameliorates carbon tetrachloride induced liver fibrosis in rats.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Nov;68:109-18. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.09.003. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26369870
-
The therapeutic effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and simvastatin in a rat model of liver fibrosis.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Jan;68(1):111-25. doi: 10.1007/s12013-013-9698-1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 23807535
-
Therapeutic effects of hepatocyte growth factor-overexpressing human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells on liver fibrosis in rats.Cell Biol Int. 2014 Jan;38(1):106-16. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10186. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Cell Biol Int. 2014. PMID: 24115681
References
-
- Standring S, Anand N, Birch R, Collins P, Crossman R, Gleeson M, et al. Gray's Anatomy, The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. Ch. 67. USA: Elsevier; 2016. Liver; pp. 1160–71.
-
- Ovalle W, Nahirney P. Netter's Essential Histology: With Correlated Histopathology. 3rd ed. Vol. 14. China: Elsevier; 2021. Liver, gallbladder, and exocrine pancreas; pp. 334–46.
-
- Pandit A, Sachdeva T, Bafna P. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Appl Pharm Sci. 2012;2:233–43.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
