Management of complications following implant-based breast reconstruction: a narrative review
- PMID: 38213810
- PMCID: PMC10777227
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-23-1384
Management of complications following implant-based breast reconstruction: a narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: Complications associated with implant-based reconstruction have a spectrum of severity with sequelae ranging from mild aesthetic deformities to additional surgery, reconstructive failure and systemic illness. The purpose of this narrative review of the literature is to provide updated evidence-based information on the management of complications in implant-based reconstruction.
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, OVID MEDLINE and the Cochrane Library databases was performed to identify common complications associated with implant-based breast reconstruction, incidences of occurrence as well as preventative and management strategies.
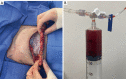
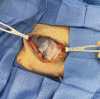
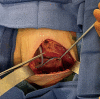
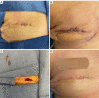
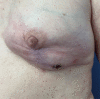
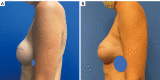
Key content and findings: Pertinent short and long-term complications of implant-based breast reconstruction include hematoma, implant infection, seroma, skin envelope necrosis, capsular contracture, rupture, malposition, animation and contour deformities, implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and breast implant illness. Important preventative measures for short term complications include meticulous sterile technique and antibiotic irrigation, adequate drainage and critical evaluation of mastectomy flaps. Management of short-term complications requires early recognition and aggressive treatment to prevent reconstructive failure as well as long-term complications such as capsular contracture. Important technological advances include dual-port expanders for seroma drainage, indocyanine green angiography for mastectomy flap perfusion evaluation, cohesive form-stable implants for treatment of rippling, and various biologic and synthetic mesh products for pocket control and correction.
Conclusions: Important principles in management of short-term complications in implant-based reconstruction include aggressive and early intervention to maximize the chance of reconstructive salvage. Contemporary technological advances have played an important role in both prevention and treatment of complications. Over-arching principles in management of implant-based reconstruction complications focus on preventative techniques and preoperative patient counseling on potential risks, their likelihood, and necessary treatments to allow for informed and shared decision-making.
Keywords: Breast reconstruction; breast implants; complications.
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-23-1384/coif). The series “Breast Reconstruction” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Timing of Acute and Late Complications Following Mastectomy and Implant-based Reconstruction.Ann Surg. 2023 Jul 1;278(1):e203-e208. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005574. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Ann Surg. 2023. PMID: 35837894
-
The Impact of Premastectomy Versus Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy on Outcomes in Prepectoral Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction.Ann Plast Surg. 2021 Jul 1;87(1s Suppl 1):S21-S27. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002801. Ann Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 33833185
-
Comprehensive Comparison Between Shaped Versus Round Implants for Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Aesthet Surg J. 2021 Jan 1;41(1):34-44. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjaa128. Aesthet Surg J. 2021. PMID: 32449906
-
Complications Including Capsular Contracture in Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction With Textured Anatomical Versus Smooth Round Implants: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis.J Breast Cancer. 2023 Feb;26(1):25-34. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2023.26.e7. J Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36852965 Free PMC article.
-
Indocyanine green angiography for preventing postoperative mastectomy skin flap necrosis in immediate breast reconstruction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 22;4(4):CD013280. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013280.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32320056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Von Willebrand's disease in breast surgery: case report.J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Jun 4;2024(6):rjae395. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjae395. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38835948 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Potential of Drain Tip Cultures: Impact on Surgical Site Infections in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction.J Breast Cancer. 2024 Aug;27(4):248-259. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2024.0045. Epub 2024 Jul 29. J Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39069783 Free PMC article.
-
Single stage direct -to- implant breast reconstruction following mastectomy (The use of Ultrapro® Mesh).World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Nov 12;22(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03576-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39533342 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring and Management of Infection following Prepectoral Implant-based Breast Reconstruction: Retrospective Analysis of Conservative Treatment Versus Implant Removal.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 Feb 5;13(2):e6516. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006516. eCollection 2025 Feb. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 39911536 Free PMC article.
-
Mastectomy Skin Flap Perfusion Assessment Prior to Breast Reconstruction: A Narrative Review.J Pers Med. 2024 Sep 6;14(9):946. doi: 10.3390/jpm14090946. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39338200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic Surgery Statistics Report: ASPS National Clearinghouse of Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. 2020. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2020/plastic-su...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
