Discovery of Potent Antimalarial Type II Kinase Inhibitors with Selectivity over Human Kinases
- PMID: 38214254
- PMCID: PMC10950204
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02046
Discovery of Potent Antimalarial Type II Kinase Inhibitors with Selectivity over Human Kinases
Abstract
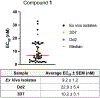
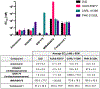
While progress has been made in the effort to eradicate malaria, the disease remains a significant threat to global health. Acquired resistance to frontline treatments is emerging in Africa, urging a need for the development of novel antimalarial agents. Repurposing human kinase inhibitors provides a potential expedited route given the availability of a diverse array of kinase-targeting drugs that are approved or in clinical trials. Phenotypic screening of a library of type II human kinase inhibitors identified compound 1 as a lead antimalarial, which was initially developed to target human ephrin type A receptor 2 (EphA2). Here, we report a structure-activity relationship study and lead optimization of compound 1, which led to compound 33, with improved antimalarial activity and selectivity.
Figures




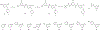
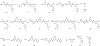

References
-
- World Malaria Report 2022; World Health Organization, 2022.
-
- Uwimana A; Legrand E; Stokes BH; Ndikumana JM; Warsame M; Umulisa N; Ngamije D; Munyaneza T; Mazarati JB; Munguti K; et al. Emergence and clonal expansion of in vitro artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum kelch13 R561H mutant parasites in Rwanda. Nat. Med 2020, 26 (10), 1602–1608. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayala-Aguilera CC; Valero T; Lorente-Macias A; Baillache DJ; Croke S; Unciti-Broceta A Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitor Drugs (1995–2021): Medical Indication, Pharmacology, and Synthesis. J. Med. Chem 2022, 65 (2), 1047–1131. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson FM; Gray NS Kinase inhibitors: the road ahead. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2018, 17 (5), 353–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

