Regulator of G protein signalling 18 promotes osteocyte proliferation by activating the extracellular signal‑regulated kinase signalling pathway
- PMID: 38214344
- PMCID: PMC10836495
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5346
Regulator of G protein signalling 18 promotes osteocyte proliferation by activating the extracellular signal‑regulated kinase signalling pathway
Abstract
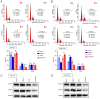
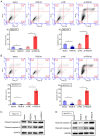
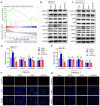
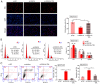
Osteocyte function is critical for metabolism, remodelling and regeneration of bone tissue. In the present study, the roles of regulator of G protein signalling 18 (RGS18) were assessed in the regulation of osteocyte proliferation and bone formation. Target genes and signalling pathways were screened using the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). The function of RGS18 and the associated mechanisms were analysed by Cell Counting Kit 8 assay, 5‑ethynyl‑2'‑deoxyuridine assay, flow cytometry, reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR, western blotting and immunostaining. Overlap analysis of acutely injured subjects (AIS) and healthy volunteers (HVs) from the GSE93138 and GSE93215 datasets of the GEO database identified four genes: KIAA0825, ANXA3, RGS18 and LIPN. Notably, RGS18 was more highly expressed in peripheral blood samples from AIS than in those from HVs. Furthermore, RGS18 overexpression promoted MLO‑Y4 and MC3T3‑E1 cell viability, proliferation and S‑phase arrest, but inhibited apoptosis by suppressing caspase‑3/9 cleavage. Silencing RGS18 exerted the opposite effects. GSEA of GSE93138 revealed that RGS18 has the ability to regulate MAPK signalling. Treatment with the MEK1/2 inhibitor PD98059 reversed the RGS18 overexpression‑induced osteocyte proliferation, and treatment with the ERK1/2 activator 12‑O‑tetradecanoylphorbol‑13‑acetate reversed the effects of RGS18 silencing on osteocyte proliferation. In conclusion, RGS18 may contribute to osteocyte proliferation and bone fracture healing via activation of ERK signalling.
Keywords: bone fracture; extracellular signal‑regulated kinase signalling; osteocytes; proliferation; regulator of G protein signalling 18.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RGS18 is a myeloerythroid lineage-specific regulator of G-protein-signalling molecule highly expressed in megakaryocytes.Biochem J. 2001 Oct 1;359(Pt 1):109-18. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3590109. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11563974 Free PMC article.
-
RGS18 acts as a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis by modulating the acid-sensing OGR1/NFAT signaling pathway.J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Oct;22(10):1612-20. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.070612. J Bone Miner Res. 2007. PMID: 17576169
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel regulator of G-protein signaling from mouse hematopoietic stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 12;276(2):915-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005947200. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11042171
-
How much do we know about the role of osteocytes in different phases of fracture healing? A systematic review.J Orthop Translat. 2019 Aug 8;21:111-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2019.07.005. eCollection 2020 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2019. PMID: 32309136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteocyte function, osteocyte death and bone fracture resistance.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000 Jan 25;159(1-2):7-13. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(99)00174-4. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10687847 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism study of YangJing ZhongYu decoction on regulating mitochondrial dynamics of ovarian granular cells and improving diminished ovarian reserve.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Sep 17;17(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01506-0. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 39289738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreev D, Liu M, Weidner D, Kachler K, Faas M, Grüneboom A, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Muñoz LE, Steffen U, Grötsch B, et al. Osteocyte necrosis triggers osteoclast-mediated bone loss through macrophage-inducible C-type lectin. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:4811–4830. doi: 10.1172/JCI134214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

