A nomogram based on ultrasound scoring system for differentiating between immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis and primary Sjögren syndrome
- PMID: 38214944
- PMCID: PMC11003662
- DOI: 10.1093/dmfr/twad005
A nomogram based on ultrasound scoring system for differentiating between immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis and primary Sjögren syndrome
Abstract
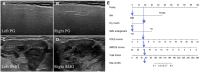
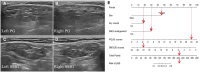
Objectives: Accurate distinguishing between immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis (IgG4-RS) and primary Sjögren syndrome (pSS) is crucial due to their different treatment approaches. This study aimed to construct and validate a nomogram based on the ultrasound (US) scoring system for the differentiation of IgG4-RS and pSS.
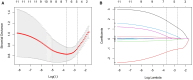
Methods: A total of 193 patients with a clinical diagnosis of IgG4-RS or pSS treated at our institution were enrolled in the training cohort (n = 135; IgG4-RS = 28, pSS = 107) and the validation cohort (n = 58; IgG4-RS = 15, pSS = 43). The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression algorithm was utilized to screen the most optimal clinical features and US scoring parameters. A model for the differential diagnosis of IgG4-RS or pSS was built using logistic regression and visualized as a nomogram. The performance levels of the nomogram model were evaluated and validated in both the training and validation cohorts.
Results: The nomogram incorporating clinical features and US scoring parameters showed better predictive value in differentiating IgG4-RS from pSS, with the area under the curves of 0.947 and 0.958 for the training cohort and the validation cohort, respectively. Decision curve analysis demonstrated that the nomogram was clinically useful.
Conclusions: A nomogram based on the US scoring system showed favourable predictive efficacy in differentiating IgG4-RS from pSS. It has the potential to aid in clinical decision-making.
Keywords: immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis; nomogram; primary Sjögren syndrome; salivary gland; ultrasound scoring system.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology and the International Association of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors of this article have reported no disclosures.
Figures


References
-
- Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, Stone JH.. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(12):1203-1210. https://doi.org10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.013 - PubMed
-
- Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(9):1181-1192. https://doi.org10.1038/modpathol.2012.72 - PubMed
-
- Mulholland GB, Jeffery CC, Satija P, Côté DW.. Immunoglobulin G4-related diseases in the head and neck: a systematic review. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;44(1):24. https://doi.org10.1186/s40463-015-0071-9 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatzis LG, Stergiou IE, Goules AV, et al. Clinical picture, outcome and predictive factors of lymphoma in primary Sjögren's syndrome: results from a harmonized dataset (1981-2021). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022;61(9):3576-3585. https://doi.org10.1093/rheumatology/keab939 - PubMed
-
- Fragoulis GE, Zampeli E, Moutsopoulos HM.. IgG4-related sialadenitis and Sjögren's syndrome. Oral Dis. 2017;23(2):152-156. https://doi.org10.1111/odi.12526 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

