Near-Infrared Induced miR-34a Delivery from Nanoparticles in Esophageal Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 38215360
- PMCID: PMC11032112
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202303593
Near-Infrared Induced miR-34a Delivery from Nanoparticles in Esophageal Cancer Treatment
Abstract
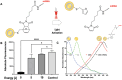
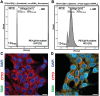
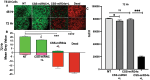
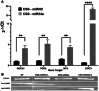
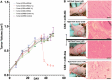
Current nucleic acid delivery methods have not achieved efficient, non-toxic delivery of miRNAs with tumor-specific selectivity. In this study, a new delivery system based on light-inducible gold-silver-gold, core-shell-shell (CSS) nanoparticles is presented. This system delivers small nucleic acid therapeutics with precise spatiotemporal control, demonstrating the potential for achieving tumor-specific selectivity and efficient delivery of miRNA mimics. The light-inducible particles leverage the photothermal heating of metal nanoparticles due to the local surface plasmonic resonance for controlled chemical cleavage and release of the miRNA mimic payload. The CSS morphology and composition result in a plasmonic resonance within the near-infrared (NIR) region of the light spectrum. Through this method, exogenous miR-34a-5p mimics are effectively delivered to human squamous cell carcinoma TE10 cells, leading to apoptosis induction without adverse effects on untransformed keratinocytes in vitro. The CSS nanoparticle delivery system is tested in vivo in Foxn1nu athymic nude mice with bilateral human esophageal TE10 cancer cells xenografts. These experiments reveal that this CSS nanoparticle conjugates, when systemically administered, followed by 850 nm light emitting diode irradiation at the tumor site, 6 h post-injection, produce a significant and sustained reduction in tumor volume, exceeding 87% in less than 72 h.
Keywords: Diels–Alder; esophageal cancer; miR‐34a; near‐infrared; plasmonic nanoparticles.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Trotti A., Byhardt R., Stetz J., Gwede C., Corn B., Fu K., Gunderson L., McCormick B., Morrisintegral M., Rich T., Shipley W., Curran W., Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2000, 47, 13. - PubMed
-
- Carelle N., Piotto E., Bellanger A., Germanaud J., Thuillier A., Khayat D., Cancer 2002, 95, 155. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2022, American Cancer Society, 2022, https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer‐facts‐statistics/all‐cancer‐facts... (accessed: Febuary 2023).
-
- Wang Y., Grainger D. W., Front Chem Sci Eng 2014, 8, 265.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

