Follow-up from the A041202 study shows continued efficacy of ibrutinib regimens for older adults with CLL
- PMID: 38215395
- PMCID: PMC11103091
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2023021959
Follow-up from the A041202 study shows continued efficacy of ibrutinib regimens for older adults with CLL
Abstract
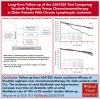
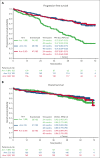
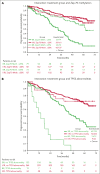
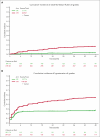
A041202 (NCT01886872) is a phase 3 study comparing bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) with ibrutinib and the combination of ibrutinib plus rituximab (IR) in previously untreated older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The initial results showed that ibrutinib-containing regimens had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and rituximab did not add additional benefits. Here we present an updated analysis. With a median follow-up of 55 months, the median PFS was 44 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 38-54) for BR and not yet reached in either ibrutinib-containing arm. The 48-month PFS estimates were 47%, 76%, and 76% for BR, ibrutinib, and IR, respectively. The benefit of ibrutinib regimens over chemoimmunotherapy was consistent across subgroups of patients defined by TP53 abnormalities, del(11q), complex karyotype, and immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IGHV). No significant interaction effects were observed between the treatment arm and del(11q), the complex karyotype, or IGHV. However, a greater difference in PFS was observed among the patients with TP53 abnormalities. There was no difference in the overall survival. Notable adverse events with ibrutinib included atrial fibrillation (afib) and hypertension. Afib was observed in 11 patients (pts) on BR (3%) and 67 pts on ibrutinib (18%). All-grade hypertension was observed in 95 pts on BR (27%) and 263 pts on ibrutinib (55%). These data show that ibrutinib regimens prolong PFS compared with BR for older patients with treatment-naïve CLL. These benefits were observed across subgroups, including high-risk groups. Strikingly, within the ibrutinib arms, there was no inferior PFS for patients with abnormalities in TP53, the highest risk feature observed in CLL. These data continue to demonstrate the efficacy of ibrutinib in treatment-naïve CLL.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.A.W. received research funding from AbbVie, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and Schrodinger and consulted for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Genentech, Loxo/Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Newave, Pharmacyclics, and Schrodinger. A.S.R. is an employee of Eli Lilly but worked at The Ohio State University without conflicts at the time of this work. C.M. received research funding from AbbVie. K.A.R. received research funding from Genentech, AbbVie, Janssen, and Novartis, consulted for AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, Genentech, LOXO@Lilly, and received travel funding from AstraZeneca. S.A.P. received research funding from Janssen, AstraZeneca, Merck, and Genentech and consults for Pharmacyclics, Merck, AstraZeneca, Janssen, BeiGene, Genentech, Amgen, Mingsight, TG Therapeutics, Novalgen Limited, Kite Pharma, and AbbVie. R.M.S. consults for AbbVie, Actinium, Amgen, Aptevo, Arog, AvenCell, BerGenBio, Bristol Myers Squib, Boston Pharmaceuticals, Cellularity, CTI pharma, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Hermavant, Janssen, Jazz, Kura Onc, Ligand Pharma, Novartis, Rigel, Syros, and Takeda. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Moreno C, Greil R, Demirkan F, et al. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(1):43–56. - PubMed
-
- Shanafelt T. Treatment of older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: key questions and current answers. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2013;2013:158–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UG1 CA233331/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233320/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA232760/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233253/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180863/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233327/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

