The intersection between host-pathogen interactions and metabolism during Vibrio cholerae infection
- PMID: 38215547
- PMCID: PMC12077413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102421
The intersection between host-pathogen interactions and metabolism during Vibrio cholerae infection
Abstract
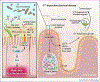
Vibrio cholerae (V. cholerae), the etiological agent of cholera, uses cholera toxin (CT) to cause severe diarrheal disease. Cholera is still a significant cause of mortality worldwide with about half of all cholera cases and deaths occurring in children under five. Owing to the lack of cost-effective vaccination and poor vaccine efficacy in children, there is a need for alternative preventative and therapeutic strategies. Recent advances in our knowledge of the interplay between CT-induced disease and host-pathogen metabolism have opened the door for investigating how modulation of intestinal metabolism by V. cholerae during disease impacts host intestinal immunity, the gut microbiota, and pathogen-phage interactions. In this review article, we examine recent progress in our understanding of host-pathogen interactions during V. cholerae infection and discuss future work deciphering how modulation of gut metabolism during cholera intersects these processes to enable successful fecal-oral transmission of the pathogen.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of Host-Microbe Metabolism by Cholera Toxin.Infect Immun. 2023 May 16;91(5):e0043522. doi: 10.1128/iai.00435-22. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 37022166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outer Membrane Vesicles of Vibrio cholerae Protect and Deliver Active Cholera Toxin to Host Cells via Porin-Dependent Uptake.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0053421. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00534-21. Epub 2021 May 26. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34076466 Free PMC article.
-
The Vibrio cholerae minor pilin TcpB mediates uptake of the cholera toxin phage CTXφ.J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 25;294(43):15698-15710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009980. Epub 2019 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31471320 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae at the Intersection of Immunity and the Microbiome.mSphere. 2019 Nov 27;4(6):e00597-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00597-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31776240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholera toxin promotes pathogen acquisition of host-derived nutrients.Nature. 2019 Aug;572(7768):244-248. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1453-3. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31367037 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

