The human vaginal microbiota: from clinical medicine to models to mechanisms
- PMID: 38215548
- PMCID: PMC11160953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102422
The human vaginal microbiota: from clinical medicine to models to mechanisms
Abstract
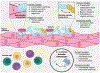
The composition of the vaginal microbiota is linked to numerous reproductive health problems, including increased susceptibility to infection, pregnancy complications, and impaired vaginal tissue repair; however, the mechanisms contributing to these adverse outcomes are not yet fully defined. In this review, we highlight recent clinical advancements associating vaginal microbiome composition and function with health outcomes. Subsequently, we provide a summary of emerging models employed to identify microbe-microbe interactions contributing to vaginal health, including metagenomic sequencing, multi-omics approaches, and advances in vaginal microbiota cultivation. Last, we review new in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo models, such as organoids and humanized microbiota murine models, used to define and mechanistically explore host-microbe interactions at the vaginal mucosa.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Hugenholtz F, van der Veer C, Terpstra ML, Borgdorff H, van Houdt R, Bruisten S, Geerlings SE, van de Wijgert JHHM: Urine and vaginal microbiota compositions of postmenopausal and premenopausal women differ regardless of recurrent urinary tract infection and renal transplant status. Sci Rep 2022, 12. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brotman RM, Shardell MD, Gajer P, Fadrosh D, Chang K, Silver MI, Viscidi RP, Burke AE, Ravel J, Gravitt PE: Association between the vaginal microbiota, menopause status, and signs of vulvovaginal atrophy. Menopause 2014, 21:1321–1330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

