Pulmonary blood flow in children with univentricular heart and unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis
- PMID: 38216538
- PMCID: PMC10809914
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivae011
Pulmonary blood flow in children with univentricular heart and unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis
Abstract
Objectives: Spontaneous breathing has an important effect on pulmonary arterial blood flow in patients with Glenn/Fontan circulation. Unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis (DP) is a frequent complication after heart surgery in congenital heart disease. The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of unilateral DP on blood flow distribution in the pulmonary arteries with Glenn/Fontan circulation.
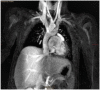
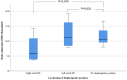
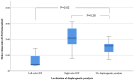
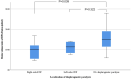
Methods: Magnetic resonance phase-contrast imaging was used to evaluate stroke volume index (SVI) in the left and right pulmonary arteries in patients with Glenn/Fontan circulation with unilateral DP. Data for 18 patients with univentricular heart and unilateral DP were analysed, 8 in the Glenn stage and 10 in the Fontan stage. Ten patients had right-sided DP, and 8 had left-sided DP. A diaphragmatic plication was performed in 7 patients. The control group consisted of 36 patients with Glenn (n = 16)/Fontan (n = 20) circulation without DP.
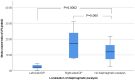
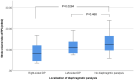
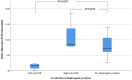
Results: In both left- and right-sided DP, the SVI to the ipsilateral side was significantly lower than in controls [2.81 (1.45-4.50) ml/m2 left vs 11.97 (7.36-16.37) ml/m2 in controls, P < 0.0002; 8.2 (4.49-12.64) ml/m2 with right vs 12.64 (9.66-16.61) ml/m2 in controls; P = 0.0284]. The SVI to the contralateral side showed a slight but non-significant increase in the presence of unilateral DP.
Conclusions: Unilateral DP in patients with Glenn/Fontan circulation has a negative impact on pulmonary arterial SVI on the side of the paralysis.
Keywords: Congenital heart disease; Diaphragmatic paralysis; Fontan; Glenn; Pulmonary blood flow.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.
Figures
References
-
- de Leval MR, Kilner P, Gewillig M, Bull C, McGoon DC.. Total cavopulmonary connection: a logical alternative to atriopulmonary connection for complex Fontan operations. Experimental studies and early clinical experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1988;96:682–95. - PubMed
-
- Hsia TY, Khambadkone S, Redington AN, Migliavacca F, Deanfield JE, de Leval MR.. Effects of respiration and gravity on infradiaphragmatic venous flow in normal and Fontan patients. Circulation 2000;102:III148–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

