Klf10 is involved in extracellular matrix calcification of chondrocytes alleviating chondrocyte senescence
- PMID: 38217021
- PMCID: PMC10790269
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04666-7
Klf10 is involved in extracellular matrix calcification of chondrocytes alleviating chondrocyte senescence
Abstract
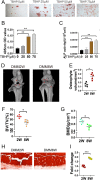
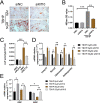
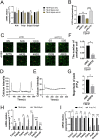
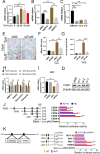
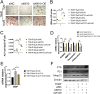
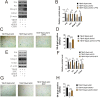
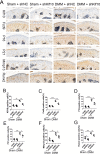
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic degenerative disease resulting joint disability and pain. Accumulating evidences suggest that chondrocyte extracellular matrix calcification plays an important role in the development of OA. Here, we showed that Krüppel-like factor 10 (Klf10) was involved in the regulation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix calcification by regulating the expression of Frizzled9. Knockdown of Klf10 attenuated TBHP induced calcification and reduced calcium content in chondrocytes. Restoring extracellular matrix calcification of chondrocytes could aggravate chondrocyte senescence. Destabilization of a medial meniscus (DMM) mouse model of OA, in vivo experiments revealed that knockdown Klf10 improved the calcification of articular cartilage and ameliorated articular cartilage degeneration. These findings suggested that knockdown Klf10 inhibited extracellular matrix calcification-related changes in chondrocytes and alleviated chondrocyte senescence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Klf10 Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence of Chondrocytes via Modulating Mitophagy.Molecules. 2023 Jan 17;28(3):924. doi: 10.3390/molecules28030924. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770589 Free PMC article.
-
KLF10 is upregulated in osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte proliferation and migration by upregulating Acvr1 and suppressing inhbb expression.Acta Histochem. 2020 Apr;122(3):151528. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151528. Epub 2020 Mar 8. Acta Histochem. 2020. PMID: 32156482
-
SERPINF1 knockdown attenuates chondrocyte senescence, hypertrophy, and inflammation in osteoarthritis to offer a potential therapeutic strategy.Cell Signal. 2025 Aug;132:111840. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111840. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40306348
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying the Aging of Articular Cartilage and Osteoarthritis.Gerontology. 2019;65(4):387-396. doi: 10.1159/000496688. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Gerontology. 2019. PMID: 30970348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of shear stress on articular chondrocyte metabolism.Biorheology. 2000;37(1-2):95-107. Biorheology. 2000. PMID: 10912182 Review.
Cited by
-
CPP-calcification of articular cartilage is associated with elevated cytokine levels in synovial fluid.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 19;13:1535530. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1535530. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40177128 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key biomarkers related to fibrocartilage chondrocytes for osteoarthritis based on bulk, single-cell transcriptomic data.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 21;15:1482361. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1482361. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39640258 Free PMC article.
-
Guilu Erxian glue reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and restores the balance of extracellular matrix synthesis and degradation in chondrocytes by inhibiting the ATF6/GRP78/CHOP signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 31;10(24):e39987. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39987. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39759286 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81572174/Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772384/Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81902242/Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021A1515010531/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2021A1515010621/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

