Enhanced deep learning model enables accurate alignment measurement across diverse institutional imaging protocols
- PMID: 38217058
- PMCID: PMC10785531
- DOI: 10.1186/s43019-023-00209-y
Enhanced deep learning model enables accurate alignment measurement across diverse institutional imaging protocols
Abstract
Background: Achieving consistent accuracy in radiographic measurements across different equipment and protocols is challenging. This study evaluates an advanced deep learning (DL) model, building upon a precursor, for its proficiency in generating uniform and precise alignment measurements in full-leg radiographs irrespective of institutional imaging differences.
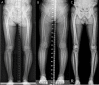
Methods: The enhanced DL model was trained on over 10,000 radiographs. Utilizing a segmented approach, it separately identified and evaluated regions of interest (ROIs) for the hip, knee, and ankle, subsequently integrating these regions. For external validation, 300 datasets from three distinct institutes with varied imaging protocols and equipment were employed. The study measured seven radiologic parameters: hip-knee-ankle angle, lateral distal femoral angle, medial proximal tibial angle, joint line convergence angle, weight-bearing line ratio, joint line obliquity angle, and lateral distal tibial angle. Measurements by the model were compared with an orthopedic specialist's evaluations using inter-observer and intra-observer intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs). Additionally, the absolute error percentage in alignment measurements was assessed, and the processing duration for radiograph evaluation was recorded.
Results: The DL model exhibited excellent performance, achieving an inter-observer ICC between 0.936 and 0.997, on par with an orthopedic specialist, and an intra-observer ICC of 1.000. The model's consistency was robust across different institutional imaging protocols. Its accuracy was particularly notable in measuring the hip-knee-ankle angle, with no instances of absolute error exceeding 1.5 degrees. The enhanced model significantly improved processing speed, reducing the time by 30-fold from an initial 10-11 s to 300 ms.
Conclusions: The enhanced DL model demonstrated its ability for accurate, rapid alignment measurements in full-leg radiographs, regardless of protocol variations, signifying its potential for broad clinical and research applicability.
Keywords: Accuracy; Alignment measurement; Deep learning; Full-leg radiographs; Imaging protocol.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.W.N is a paid employee of CONNECTEVE Co., LTD. D.H.R is CEO of CONNECTEVE Co., Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated analysis of knee joint alignment using detailed angular values in long leg radiographs based on deep learning.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;14(1):7226. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57887-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38538685 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based landmark recognition and angle measurement of full-leg plain radiographs can be adopted to assess lower extremity alignment.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 Apr;31(4):1388-1397. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-07124-x. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 36006418
-
Artificial intelligence-based analyses of varus leg alignment and after high tibial osteotomy show high accuracy and reproducibility.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 Dec;31(12):5885-5895. doi: 10.1007/s00167-023-07644-0. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 37975938 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and interobserver reliability analysis of pediatric lower limb parameters on digital long leg radiographs.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jan 27;18(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03552-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36707864 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Double and Single Leg Weight-Bearing Radiography in Determining Knee Alignment.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017 May;5(3):174-180. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017. PMID: 28656165 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Automated analysis of knee joint alignment using detailed angular values in long leg radiographs based on deep learning.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;14(1):7226. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57887-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38538685 Free PMC article.
-
Association of radiographic structure deformity phenotypes of knee OA to clinical symptoms and risk for progression: Proposing a modification of Kellgren-Lawrence grade - Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative and the MOST study.Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2025 Jan 9;7(1):100566. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2025.100566. eCollection 2025 Mar. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2025. PMID: 39896932 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensionally Measured TT-TG Distance Remains After Medial Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy and Correlates With Internal Rotation of Distal Tibial Segment Below the Osteotomy Site.Cartilage. 2025 Mar 26:19476035251327025. doi: 10.1177/19476035251327025. Online ahead of print. Cartilage. 2025. PMID: 40138459 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a deep learning software for automated measurements on full-leg standing radiographs.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024 Nov 29;36(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s43019-024-00246-1. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39614404 Free PMC article.
-
Automated radiographic assessment of lower limb alignment using deep learning in a data-constrained clinical setting.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jul 4;26(1):603. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08846-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40615817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tack A, Preim B, Zachow S. Fully automated Assessment of Knee Alignment from Full-Leg X-Rays employing a "YOLOv4 And Resnet Landmark regression Algorithm" (YARLA): Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;205:106080. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106080. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

