Adaptive behavior assessed by Vineland-3 as comprehensive outcome measure in vanishing white matter
- PMID: 38217081
- PMCID: PMC10963295
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51985
Adaptive behavior assessed by Vineland-3 as comprehensive outcome measure in vanishing white matter
Abstract
Objectives: Investigate the results and usability of the Vineland-3 as an outcome measure in vanishing white matter patients.
Methods: A cross-sectional investigation of the Vineland-3 based on interviews with caregivers, the Health Utilities Index, and the modified Rankin Scale in 64 vanishing white matter patients.
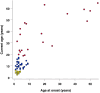
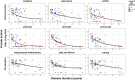
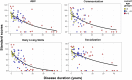
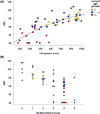
Results: Adaptive behavior measured with the Vineland-3 is impaired in the vast majority of vanishing white matter patients and significantly impacts daily life. Typically, the daily living skills domain is most severely affected and the socialization domain is the least affected. Based on the metric properties and the clinical relevance, the standard scores for the daily living skills domain and Adaptive Behavior Composite have the best properties to be used as an outcome measure.
Interpretation: The Vineland-3 appears to be a useful outcome measure to explore and quantify complex cognitive, behavioral, and psychiatric impairments affecting daily functioning in vanishing white matter. Further research should address the longitudinal evaluation of this tool and its additional value to standard neuropsychological and clinical examination.
© 2024 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
MSvdK: consultant for Calico (VWM) and coinvestigator for Ionis (Alexander disease trial), without personal payment. She is on patent P112686US00 “therapeutic effects of Guanabenz treatment in vanishing white matter” and on patent P112686CA00 “the use of Guanabenz in the treatment of VWM,” both for the VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. She is the initiator and principal investigator of the Guanabenz trial (
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale in a Cohort of Four ADNP Syndrome Patients Implicates Age-Dependent Developmental Delays with Increased Impact of Activities of Daily Living.J Mol Neurosci. 2022 Aug;72(8):1531-1546. doi: 10.1007/s12031-022-02048-0. Epub 2022 Aug 3. J Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35920977
-
Adaptive behavior in autism: Minimal clinically important differences on the Vineland-II.Autism Res. 2018 Feb;11(2):270-283. doi: 10.1002/aur.1874. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Autism Res. 2018. PMID: 28941213 Free PMC article.
-
Brief report: adaptive behavior and cognitive skills for toddlers on the autism spectrum.J Autism Dev Disord. 2011 May;41(5):679-84. doi: 10.1007/s10803-010-1083-y. J Autism Dev Disord. 2011. PMID: 20697794 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal assessment of adaptive behavior in infants and young children with newly diagnosed epilepsy: influences of etiology, syndrome, and seizure control.Pediatrics. 2004 Sep;114(3):645-50. doi: 10.1542/peds.2003-1151-L. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15342834
-
Review of adaptive behavior studies in mentally retarded persons with autism/pervasive developmental disorder.J Autism Dev Disord. 2000 Feb;30(1):39-47. doi: 10.1023/a:1005460027636. J Autism Dev Disord. 2000. PMID: 10819119 Review.
Cited by
-
ARSA Variants Associated With Cognitive Decline and Long-Term Preservation of Motor Function in Metachromatic Leukodystrophy.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2025 Sep;48(5):e70072. doi: 10.1002/jimd.70072. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2025. PMID: 40751594 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive and Adaptive Functioning of CTNNB1 Syndrome Patients: A Comparison With Autism Spectrum Disorder and Cerebral Palsy.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2025 Jul;69(7):558-568. doi: 10.1111/jir.13235. Epub 2025 Mar 27. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2025. PMID: 40145647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Knaap MS, Pronk JC, Scheper GC. Vanishing white matter disease. The Lancet Neurology. 2006;5(5):413‐423. - PubMed
-
- van der Knaap MS, Leegwater PA, Könst AA, et al. Mutations in each of the five subunits of translation initiation factor eIF2B can cause leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Ann Neurol. 2002;51(2):264‐270. - PubMed
-
- Leegwater PA, Vermeulen G, Konst AA, et al. Subunits of the translation initiation factor eIF2B are mutant in leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Nat Genet. 2001;29(4):383‐388. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

