Cellular metabolism: A key player in cancer ferroptosis
- PMID: 38217522
- PMCID: PMC10876208
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12519
Cellular metabolism: A key player in cancer ferroptosis
Abstract
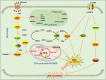
Cellular metabolism is the fundamental process by which cells maintain growth and self-renewal. It produces energy, furnishes raw materials, and intermediates for biomolecule synthesis, and modulates enzyme activity to sustain normal cellular functions. Cellular metabolism is the foundation of cellular life processes and plays a regulatory role in various biological functions, including programmed cell death. Ferroptosis is a recently discovered form of iron-dependent programmed cell death. The inhibition of ferroptosis plays a crucial role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. However, the role of cellular metabolism, particularly glucose and amino acid metabolism, in cancer ferroptosis is not well understood. Here, we reviewed glucose, lipid, amino acid, iron and selenium metabolism involvement in cancer cell ferroptosis to elucidate the impact of different metabolic pathways on this process. Additionally, we provided a detailed overview of agents used to induce cancer ferroptosis. We explained that the metabolism of tumor cells plays a crucial role in maintaining intracellular redox homeostasis and that disrupting the normal metabolic processes in these cells renders them more susceptible to iron-induced cell death, resulting in enhanced tumor cell killing. The combination of ferroptosis inducers and cellular metabolism inhibitors may be a novel approach to future cancer therapy and an important strategy to advance the development of treatments.
Keywords: cancer therapy; cellular metabolism; ferroptosis; ferroptosis inducer.
© 2024 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(5):280–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82203233/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82202966/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173142/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82302987/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82303534/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81972636/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023JJ60469/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2023JJ40413/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2023JJ30372/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2023JJ30375/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2022JJ80078/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2020JJ5336/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 202203034978/Research Project of Health Commission of Hunan Province
- 202109031837/Research Project of Health Commission of Hunan Province
- 20201020/Research Project of Health Commission of Hunan Province
- 2022SK2051/Key Research and Development Program of Hunan Province
- 2020TP1018/Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- kh2201054/Changsha Science and Technology Board
- kq2014209/Changsha Municipal Natural Science Foundation
- NCC201909B06/Ascend Foundation of National Cancer Center
- ZX2020001-3/Hunan Cancer Hospital Climb Plan
- YF2020002/Hunan Cancer Hospital Climb Plan
- 2023RC3199/Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 2023SK4034/Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 2023RC1073/Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 2022TQ0104/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2022M721118/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

