The Role of Impaired Receptor Trafficking in Mediating the Pathological Effects of APOE4 in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 38217595
- PMCID: PMC10894586
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-230514
The Role of Impaired Receptor Trafficking in Mediating the Pathological Effects of APOE4 in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) is the most prevalent genetic risk factor of Alzheimer's disease. Several studies suggest that APOE4 binding to its receptors is associated with their internalization and accumulation in intracellular compartments. Importantly, this phenomenon also occurs with other, non-ApoE receptors. Based on these observations, we hypothesized that APOE4 pathological effects are mediated by impairment in the life cycle of distinct receptors (APOER2, LRP1, IR, VEGFR).
Objective: To examine the effects of APOE genotype on receptors protein levels and compartmentalization.
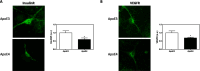
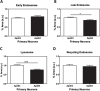
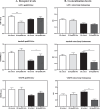
Methods: Primary mouse neurons were prepared from APOE3 or APOE4 targeted replacement mice, or APOE-KO mice. Specific receptors protein levels were evaluated in these neurons, utilizing immunofluorescent staining. Additionally, surface membrane protein levels of those receptors were assessed by cell surface biotinylation assay and ELISA. Receptors' colocalization with intracellular compartments was assessed by double staining and confocal microscopy, followed by colocalization analysis. Finally, LRP1 or APOER2 were knocked-down with CRISPR/Cas9 system to examine their role in mediating APOE4 effects on the receptors.
Results: Our results revealed lower receptors' levels in APOE4, specifically on the membrane surface. Additionally, APOE4 affects the compartmentation of these receptors in two patterns: the first was observed with LRP1 and was associated with decreased receptor levels in numerous intracellular compartments. The second was obtained with the other receptors and was associated with their accumulation in early endosomes and their decrease in the late endosomes.
Conclusions: These results provide a unifying mechanism, in which APOE4 drives the down regulation of various receptors, which plays important roles in distinct APOE4 related pathological processes.
Keywords: ABCA1; APOE4 pathology; APOER2; Alzheimer’s disease; Apolipoprotein E4; LRP1; VEGFR; insulin receptors; lipidation; receptor recycling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Involvement of the Apoer2 and Lrp1 receptors in mediating the pathological effects of ApoE4 in vivo.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014;11(6):549-57. doi: 10.2174/1567205010666131119232444. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014. PMID: 24251389 Free PMC article.
-
Central and Peripheral Mechanisms in ApoE4-Driven Diabetic Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 14;21(4):1289. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041289. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32075060 Free PMC article.
-
Abca1 deficiency affects Alzheimer's disease-like phenotype in human ApoE4 but not in ApoE3-targeted replacement mice.J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;32(38):13125-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1937-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22993429 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 May;138:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104795. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32036033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Contributions of the Endolysosomal Compartment and Autophagy to APOEɛ4 Allele-Mediated Increase in Alzheimer's Disease Risk.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;97(3):1007-1031. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230658. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38306054 Review.
Cited by
-
OCRL1 Deficiency Affects the Intracellular Traffic of ApoER2 and Impairs Reelin-Induced Responses.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 5;14(7):799. doi: 10.3390/biom14070799. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062513 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted roles of apolipoprotein E4 in Alzheimer's disease pathology and potential therapeutic strategies.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jul 8;11(1):312. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02600-y. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40628716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balin BJ, Hudson AP (2014) Etiology and pathogenesis of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 14, 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, Tanzi RE (2012) The genetics of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 107, 79–100. - PubMed
-
- Nikolac Perkovic M, Pivac N (2019) Genetic markers of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 1192, 27–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

