Illuminating function of the understudied druggable kinome
- PMID: 38218213
- PMCID: PMC11262466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.103881
Illuminating function of the understudied druggable kinome
Abstract
The human kinome, with more than 500 proteins, is crucial for cell signaling and disease. Yet, about one-third of kinases lack in-depth study. The Data and Resource Generating Center for Understudied Kinases has developed multiple resources to address this challenge including creation of a heavy amino acid peptide library for parallel reaction monitoring and quantitation of protein kinase expression, use of understudied kinases tagged with a miniTurbo-biotin ligase to determine interaction networks by proximity-dependent protein biotinylation, NanoBRET probe development for screening chemical tool target specificity in live cells, characterization of small molecule chemical tools inhibiting understudied kinases, and computational tools for defining kinome architecture. These resources are available through the Dark Kinase Knowledgebase, supporting further research into these understudied protein kinases.
Keywords: NanoBRET; SureQuant/PRM; chemical tools; dark kinase knowledgebase; human kinome; illuminating the druggable genome; miniTurbo; understudied kinases.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest
S.M.G., D.D., T.M.W., M.B.M., R.R.T., and G.L.J. have no conflicts of interest to declare. P.K.S. is a co-founder and member of the BOD of Glencoe Software, a member of the SAB of RareCyte, NanoString and Montai Health, and a consultant for Merck; he is past member of the BOD for Applied Biomath. P.K.S. declares that none of these relationships have influenced the content of this manuscript.
Figures
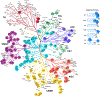


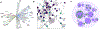

References
-
- Arencibia JM, Pastor-Flores D, Bauer AF, Schulze JO, Biondi RM. AGC protein kinases: from structural mechanism of regulation to allosteric drug development for the treatment of human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834:1302–1321. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Luo B, Lu Y, Chen Y. Targeting death-associated protein kinases for treatment of human diseases: recent advances and future directions. J Med Chem. 2023;66:1112–1136. - PubMed
-
- Ahsan R, Khan MM, Mishra A, Noor G, Ahmad U. Protein kinases and their inhibitors implications in modulating disease progression. Protein J. 2023;42:621–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

