Enrollment and clients' satisfaction with a community-based health insurance scheme: a community-based survey in Northwest Ethiopia
- PMID: 38218770
- PMCID: PMC10787395
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-10570-7
Enrollment and clients' satisfaction with a community-based health insurance scheme: a community-based survey in Northwest Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Although the Ethiopian government has implemented a community-based health insurance (CBHI) program, community enrollment and clients' satisfaction have not been well investigated in Gondar Zuria district, Northwest Ethiopia. This study assessed CBHI scheme enrollment, clients' satisfaction, and associated factors among households in the district.
Methods: A community-based cross-sectional survey assessed CBHI scheme enrollment and clients' satisfaction among households in Gondar Zuria district, Northwest Ethiopia, from May to June 2022. A systematic random sampling method was used to select the study participants from eligible households. A home-to-home interview using a structured questionnaire was conducted. Data were analysed using the statistical packages for social sciences version 26. Logistic regression was used to identify variables associated with enrollment and clients' satisfaction. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
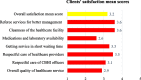
Results: Out of 410 participants, around two-thirds (64.9%) of the participants were enrolled in the CBHI scheme. Residency status (AOR = 1.38, 95% CI: 1.02-5.32; p = 0.038), time taken to reach a health facility (AOR = 1.01, 95% CI: 1.00-1.02; p = 0.001), and household size (AOR = 0.77, 95% CI: 0.67-0.88; p < 0.001) were significantly associated with CBHI scheme enrollment. Two-thirds (66.5%) of enrolled households were dissatisfied with the overall services provided; in particular, higher proportions were dissatisfied with the availability of medication and laboratory tests (88.7%). Household size (AOR = 1.31, 95% CI: 1.01-2.24; p = 0.043) and waiting time to get healthcare services (AOR = 3.14, 95% CI: 1.01-9.97; p = 0.047) were predictors of clients' satisfaction with the CBHI scheme services.
Conclusion: Although a promisingly high proportion of households were enrolled in the CBHI scheme, most of them were dissatisfied with the service. Improving waiting times to get health services, improving the availability of medications and laboratory tests, and other factors should be encouraged.
Keywords: CBHI; Community-based health insurance; Enrollment; Ethiopia; Satisfaction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Household satisfaction with community-based health insurance scheme and associated factors in piloted Sheko district; Southwest Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2019 May 13;14(5):e0216411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216411. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31083706 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Is Ethiopian community-based health insurance affordable? Willingness to pay analysis among households in South Central, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 27;17(10):e0276856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276856. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36301951 Free PMC article.
-
The level of household satisfaction with community-based health insurance and associated factors in Southern Ethiopia.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 30;11:1165441. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1165441. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37457275 Free PMC article.
-
Household satisfaction and associated factors with community-based health insurance scheme in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analysis.Glob Health Res Policy. 2023 Sep 15;8(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s41256-023-00325-y. Glob Health Res Policy. 2023. PMID: 37710337 Free PMC article.
-
Towards universal health coverage: The level and determinants of enrollment in the Community-Based Health Insurance (CBHI) scheme in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 18;17(8):e0272959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272959. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35980888 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Beneficiaries' satisfaction with health insurance and associated factors in Sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2025 Feb 7;15(2):e089029. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-089029. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39920054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McIntyre, D., Golbal Forum for Health Research; Helping Correct the 10/90 GAP. Health care financing in low and middle-income countries. Accessed on 25 Jun 2022. Available: https://www.files.ethz.ch/isn/48554/2007-06%20Health%20care%20financing.pdf.
-
- Kebede A, Gebreslassie M, Yitayal M. Willingness to pay for community based health insurance among households in the rural community of Fogera District, North West Ethiopia. Int J Economics Finance Manag Sci. 2014;2(4):263–269.
-
- Uzochukwu BS, Onwujekwe OE, Eze S, Ezuma N, Obikeze E, Onoka C. Community Based Health Insurance Scheme in Anambra State, Nigeria: an analysis of policy development, implementation and equity effects. London: Consortium for Research on Equitable Health Systems, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine; 2009. p. 1–35. Available: http://www.crehs.lshtm.ac.uk/downloads/publications/Community_based_heal....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources