Codon usage characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genome in Hemerocallis citrina
- PMID: 38218810
- PMCID: PMC10788020
- DOI: 10.1186/s12863-024-01191-4
Codon usage characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genome in Hemerocallis citrina
Abstract
Background: Hemerocallis citrina Baroni is a traditional vegetable crop widely cultivated in eastern Asia for its high edible, medicinal, and ornamental value. The phenomenon of codon usage bias (CUB) is prevalent in various genomes and provides excellent clues for gaining insight into organism evolution and phylogeny. Comprehensive analysis of the CUB of mitochondrial (mt) genes can provide rich genetic information for improving the expression efficiency of exogenous genes and optimizing molecular-assisted breeding programmes in H. citrina.
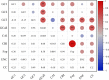
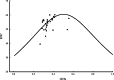
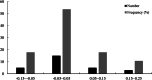
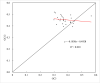
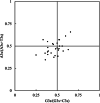
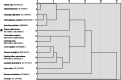
Results: Here, the CUB patterns in the mt genome of H. citrina were systematically analyzed, and the possible factors shaping CUB were further evaluated. Composition analysis of codons revealed that the overall GC (GCall) and GC at the third codon position (GC3) contents of mt genes were lower than 50%, presenting a preference for A/T-rich nucleotides and A/T-ending codons in H. citrina. The high values of the effective number of codons (ENC) are indicative of fairly weak CUB. Significant correlations of ENC with the GC3 and codon counts were observed, suggesting that not only compositional constraints but also gene length contributed greatly to CUB. Combined ENC-plot, neutrality plot, and Parity rule 2 (PR2)-plot analyses augmented the inference that the CUB patterns of the H. citrina mitogenome can be attributed to multiple factors. Natural selection, mutation pressure, and other factors might play a major role in shaping the CUB of mt genes, although natural selection is the decisive factor. Moreover, we identified a total of 29 high-frequency codons and 22 optimal codons, which exhibited a consistent preference for ending in A/T. Subsequent relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU)-based cluster and mt protein coding gene (PCG)-based phylogenetic analyses suggested that H. citrina is close to Asparagus officinalis, Chlorophytum comosum, Allium cepa, and Allium fistulosum in evolutionary terms, reflecting a certain correlation between CUB and evolutionary relationships.
Conclusions: There is weak CUB in the H. citrina mitogenome that is subject to the combined effects of multiple factors, especially natural selection. H. citrina was found to be closely related to Asparagus officinalis, Chlorophytum comosum, Allium cepa, and Allium fistulosum in terms of their evolutionary relationships as well as the CUB patterns of their mitogenomes. Our findings provide a fundamental reference for further studies on genetic modification and phylogenetic evolution in H. citrina.
Keywords: Codon usage bias; Hemerocallis citrina Baroni; Mitochondrial genome; Phylogeny.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Advances in research on the main nutritional quality of daylily, an important flower vegetable of Liliaceae.PeerJ. 2024 Aug 7;12:e17802. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17802. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39131608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Selection as the Primary Driver of Codon Usage Bias in the Mitochondrial Genomes of Three Medicago Species.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 30;16(6):673. doi: 10.3390/genes16060673. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565565 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the mitochondrial genome of Hemerocallis citrina (Asphodelaceae) using a combined assembly and comparative genomic strategy.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 18;13:1051221. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1051221. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36466251 Free PMC article.
-
Preference of A/T ending codons in mitochondrial ATP6 gene under phylum Platyhelminthes: Codon usage of ATP6 gene in Platyhelminthes.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2018 Oct;225:15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2018.08.007. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 30149040
-
Assembly and comparative analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of white towel gourd (Luffa cylindrica).Genomics. 2024 May;116(3):110859. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2024.110859. Epub 2024 May 13. Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38750703 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in research on the main nutritional quality of daylily, an important flower vegetable of Liliaceae.PeerJ. 2024 Aug 7;12:e17802. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17802. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39131608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Horizontal Transfers of Immune Genes Between Distantly Related Teleost Fishes.Mol Biol Evol. 2025 Apr 30;42(5):msaf107. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaf107. Mol Biol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40378191 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of codon usage patterns in complete plastomes of four medicinal Polygonatum species (Asparagaceae).Front Genet. 2024 Sep 19;15:1401013. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1401013. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39364010 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Selection as the Primary Driver of Codon Usage Bias in the Mitochondrial Genomes of Three Medicago Species.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 30;16(6):673. doi: 10.3390/genes16060673. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565565 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the codon usage patterns in the polyprotein coding sequences of the honeybee viruses.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 4;12:1567209. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1567209. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40687091 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
