Circulating blood biomarkers correlated with the prognosis of advanced triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 38218823
- PMCID: PMC10787989
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-023-02871-6
Circulating blood biomarkers correlated with the prognosis of advanced triple negative breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) can improve survivals of metastatic triple negative breast cancer (mTNBC); however, we still seek circulating blood biomarkers to predict the efficacy of ICIs.
Materials and methods: In this study, we analyzed the data of ICIs treated mTNBC collected in Anhui Medical University affiliated hospitals from 2018 to 2023. The counts of lymphocytes, monocytes, platelets, and ratio indexes (NLR, MLR, PLR) in peripheral blood were investigated via the Kaplan-Meier curves and the Cox proportional-hazards model.
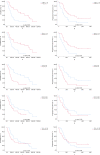
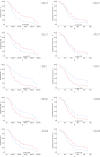
Results: The total of 50 mTNBC patients were treated with ICIs. High level of peripheral lymphocytes and low level of NLR and MLR at baseline and post the first cycle of ICIs play the predictable role of immunotherapies. Lymphocytes counts (HR = 0.280; 95% CI: 0.095-0.823; p = 0.021) and NLR (HR = 1.150; 95% CI: 1.052-1.257; p = 0.002) are significantly correlated with overall survival. High NLR also increases the risk of disease progression (HR = 2.189; 95% CI:1.085-4.414; p = 0.029). When NLR at baseline ≥ 2.75, the hazard of death (HR = 2.575; 95% CI:1.217-5.447; p = 0.013) and disease progression (HR = 2.189; 95% CI: 1.085-4.414; p = 0.029) significantly rise. HER-2 expression and anti-tumor therapy lines are statistically correlated with survivals.
Conclusions: Before the initiation of ICIs, enriched peripheral lymphocytes and poor neutrophils and NLR contribute to the prediction of survivals.
Keywords: Anti-PD-1; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immunotherapy; Peripheral blood cell count; Triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1206689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206689. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37377959 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between NLR/PLR/LMR levels and survival prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jan 21;101(3):e28617. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028617. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35060536 Free PMC article.
-
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios predict efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 7;8(1):8703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27075-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29880896 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic immune-inflammation index, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio can predict clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Oct;33(8):e22964. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22964. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 31282096 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Aug;85:106677. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106677. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32531712
Cited by
-
Serum Hepcidin Levels in Breast Cancer Patients: Investigating the Correlation to Tumor Stage-A Cross-Sectional Study.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 10;8(8):e71148. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71148. eCollection 2025 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40791284 Free PMC article.
-
Association of baseline inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 Feb 12;17:17588359251316243. doi: 10.1177/17588359251316243. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39943944 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating chemokines and leukocytes and their impact on breast cancer prognosis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 11;16(1):1060. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02881-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40500455 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia and Its Impact on Survival in Patients with Brain Metastasis.Curr Oncol. 2024 Aug 9;31(8):4559-4567. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31080340. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39195323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gonzalez-Ericsson PI, Stovgaard ES, Sua LF, Reisenbichler E, Kos Z, Carter JM, et al. The path to a better biomarker: application of a risk management framework for the implementation of PD-L1 and TILs as immuno-oncology biomarkers in breast cancer clinical trials and daily practice. J Pathol. 2020;250(5):667–84. doi: 10.1002/path.5406. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lotfinejad P, Asghari Jafarabadi M, Abdoli Shadbad M, Kazemi T, Pashazadeh F, Sandoghchian Shotorbani S, et al. Prognostic role and clinical significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): a systematic review and meta-analysis study. Diagnostics (Basel) 2020;10(9):704. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10090704. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dieci MV, Criscitiello C, Goubar A, Viale G, Conte P, Guarneri V, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on residual disease after primary chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multicenter study. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(3):611–8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

