ADAM8 silencing suppresses the migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via FSCN1/MAPK cascade in osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38218854
- PMCID: PMC10787439
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-023-03238-w
ADAM8 silencing suppresses the migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via FSCN1/MAPK cascade in osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that affects elderly populations worldwide, causing pain and disability. Alteration of the fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) phenotype leads to an imbalance in the synovial inflammatory microenvironment, which accelerates the progression of OA. Despite this knowledge, the specific molecular mechanisms of the synovium that affect OA are still unclear.
Methods: Both in vitro and in vivo experiments were undertaken to explore the role of ADAM8 playing in the synovial inflammatory of OA. A small interfering RNA (siRNA) was targeting ADAM8 to intervene. High-throughput sequencing was also used.
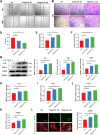
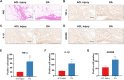
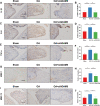
Results: Our sequencing analysis revealed significant upregulation of the MAPK signaling cascade and ADAM8 gene expression in IL-1β-induced FLSs. The in vitro results demonstrated that ADAM8 blockade inhibited the invasion and migration of IL-1β-induced FLSs, while also suppressing the expression of related matrix metallomatrix proteinases (MMPs). Furthermore, our study revealed that inhibiting ADAM8 weakened the inflammatory protein secretion and MAPK signaling networks in FLSs. Mechanically, it revealed that inhibiting ADAM8 had a significant effect on the expression of migration-related signaling proteins, specifically FSCN1. When siADAM8 was combined with BDP-13176, a FSCN1 inhibitor, the migration and invasion of FLSs was further inhibited. These results suggest that FSCN1 is a crucial downstream factor of ADAM8 in regulating the biological phenotypes of FLSs. The in vivo experiments demonstrated that ADAM8 inhibition effectively reduced synoviocytes inflammation and alleviated the progression of OA in rats.
Conclusions: ADAM8 could be a promising therapeutic target for treating OA by targeting synovial inflammation.
Keywords: ADAM8; Fibroblast-like synoviocytes; Inflammation; MAPK; Osteoarthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MAGL inhibition relieves synovial inflammation and pain via regulating NOX4-Nrf2 redox balance in osteoarthritis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Nov 1;208:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.07.019. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37516370
-
Transforming growth factor β1 promotes fibroblast-like synoviocytes migration and invasion via TGF-β1/Smad signaling in rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Sep;459(1-2):141-150. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03557-0. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31297660
-
STAT3/HIF-1α/fascin-1 axis promotes RA FLSs migration and invasion ability under hypoxia.Mol Immunol. 2022 Feb;142:83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.12.004. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34971867
-
Role and mechanism of fibroblast-activated protein-α expression on the surface of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 17;14:1135384. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135384. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A jack of all trades - ADAM8 as a signaling hub in inflammation and cancer.FEBS J. 2024 Sep;291(18):3989-4008. doi: 10.1111/febs.17034. Epub 2023 Dec 22. FEBS J. 2024. PMID: 38097912 Review.
Cited by
-
ADAM8 promotes alcoholic liver fibrosis through the MAPK signaling pathway.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Oct 16;74(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12576-024-00943-2. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39407108 Free PMC article.
-
The Integrated Transcriptome Bioinformatics Analysis of Energy Metabolism-Related Profiles for Dorsal Root Ganglion of Neuropathic Pain.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;62(4):4149-4171. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04537-2. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39406937
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82072425, 82072498, 82272157/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20220059/the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- PAPD/the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- ZD2022021/Jiangsu Medical Research Project
- BK20211083, BE2022737/the Program of Jiangsu science and technology Department
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

