Type 1 diabetes, its complications, and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy: a mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- PMID: 38218861
- PMCID: PMC10787423
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-023-02117-7
Type 1 diabetes, its complications, and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy: a mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a significant risk factor for a range of cardiovascular diseases. Nonetheless, the causal relationship between T1D and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (NICM) remains to be elucidated. Furthermore, the mechanisms responsible for the progression from T1D to NICM have not been definitively characterized.
Objective: The aim of this study was to conduct a Mendelian randomization (MR) study to investigate the causal effects of T1D and its complications on the development of NICM. Additionally, this study aimed to conduct a mediation analysis to identify potential mediators within this correlation.
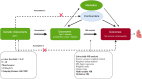
Methods: Genetic variants were used as instrumental variables for T1D. The summary data for T1D were obtained from two genome-wide association study datasets. The summary data for T1D with complications and NICM were obtained from the Finnish database. Two-sample MR, multivariable MR and mediation MR were conducted in this study.
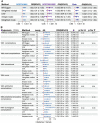
Results: The study revealed a causal association between T1D, T1D with complications, and NICM (with odds ratios of 1.02, 95% CI 1.01-1.04, p = 1.17e-04 and 1.03, 95% CI 1.01-1.05, p = 3.15e-3). Even after adjusting for confounding factors such as body mass index and hypertension, T1D remained statistically significant (with odds ratio of 1.02, 95% CI 1.01-1.04, p = 1.35e-4). Mediation analysis indicated that monokine induced by gamma interferon may play a mediating role in the pathogenesis of T1D-NICM (mediation effect indicated by odds ratio of 1.005, 95% CI 1.001-1.01, p = 4.9e-2).
Conclusion: The study demonstrates a causal relationship between T1D, its complications, and NICM. Additionally, monokine induced by gamma interferon may act as a potential mediator in the pathogenesis of T1D-NICM.
Keywords: Mediation analysis; Mendelian randomization; Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy; Type 1 diabetes; Type 1 diabetes with complication.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414:782–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus—present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8:228–36. - PubMed
-
- Katsarou A, Gudbjörnsdottir S, Rawshani A, Dabelea D, Bonifacio E, Anderson BJ, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

