Integrating bioinformatics and experimental validation to unveil disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs as prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38218909
- PMCID: PMC10788009
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-023-03208-x
Integrating bioinformatics and experimental validation to unveil disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs as prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) stands as a prevalent malignancy globally, characterized by significant morbidity and mortality. Despite continuous advancements in the treatment of HCC, the prognosis of patients with this cancer remains unsatisfactory. This study aims at constructing a disulfidoptosis‑related long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) signature to probe the prognosis and personalized treatment of patients with HCC.
Methods: The data of patients with HCC were extracted from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) databases. Univariate, multivariate, and least absolute selection operator Cox regression analyses were performed to build a disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs (DRLs) signature. Kaplan-Meier plots were used to evaluate the prognosis of the patients with HCC. Functional enrichment analysis was used to identify key DRLs-associated signaling pathways. Spearman's rank correlation was used to elucidate the association between the DRLs signature and immune microenvironment. The function of TMCC1-AS1 in HCC was validated in two HCC cell lines (HEP3B and HEPG2).
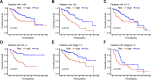
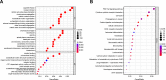
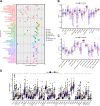
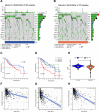
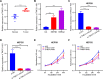
Results: We identified 11 prognostic DRLs from the TCGA dataset, three of which were selected to construct the prognostic signature of DRLs. We found that the survival time of low-risk patients was considerably longer than that of high-risk patients. We further observed that the composition and the function of immune cell subpopulations were significantly different between high- and low-risk groups. Additionally, we identified that sorafenib, 5-Fluorouracil, and doxorubicin displayed better responses in the low-score group than those in the high-score group, based on IC50 values. Finally, we confirmed that inhibition of TMCC1-AS1 impeded the proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Conclusions: The DRL signatures have been shown to be a reliable prognostic and treatment response indicator in HCC patients. TMCC1-AS1 showed potential as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: Disulfidptosis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immune microenvironment; Long non-coding RNA; Prognostic signature; TMCC1-AS1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and Validation of a Reliable Disulfidptosis-Related LncRNAs Signature of the Subtype, Prognostic, and Immune Landscape in Colon Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 18;24(16):12915. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612915. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629096 Free PMC article.
-
A disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs signature in hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic prediction, tumor immune microenvironment and drug susceptibility.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 7;14(1):746. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51459-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38185671 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a five-long non-coding RNA signature to improve the prognosis prediction for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug 14;24(30):3426-3439. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i30.3426. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30122881 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a prognostic model for disulfidptosis-related long noncoding RNAs in R0 resected hepatocellular carcinoma and analysis of their impact on malignant behavior.BMC Cancer. 2024 Aug 29;24(1):1068. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12816-3. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39210306 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related LncRNAs in Molecular Classification, Immune Microenvironment Characterization and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 28;11(12):3165. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123165. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137387 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multi‑cohort Validation Based on Disulfidptosis-Related lncRNAs for Predicting Prognosis and Immunotherapy Response of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2025 Jun 25;18:763-778. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S519270. eCollection 2025. Onco Targets Ther. 2025. PMID: 40589861 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of POLH-AS1 as a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 6;24(1):1112. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12857-8. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39242532 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfidptosis in tumor progression.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Apr 28;11(1):205. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02495-9. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40295497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs cluster to forecast the prognosis and immune landscapes of ovarian cancer.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 9;15:1397011. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1397011. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39045330 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of disulfidptosis-associated genes in gastric cancer: a comprehensive analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 4;15:1512394. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1512394. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40104507 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

