Varus placement of the tibial component reduces the potential risk of fracture with adequate bony coverage in the Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 38218913
- PMCID: PMC10787735
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-48659-4
Varus placement of the tibial component reduces the potential risk of fracture with adequate bony coverage in the Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
Abstract
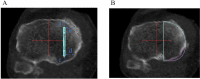
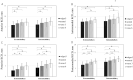
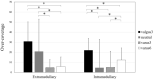
A short keel-cortex distance (KCD), especially to the posterior cortex, is a potential risk factor for tibial plateau fracture after Oxford mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (OUKA). This study aimed to evaluate the effect of tibial component alignment in the coronal plane and tibial proximal morphology on the KCD. Included in this study were 51 patients scheduled for primary Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA). The anterior and posterior KCD were preoperatively assessed using 3D simulation software with the component set perpendicular to the tibial mechanical axis (neutral), 3° valgus, 3° varus, and 6° varus, relative to neutral alignment. We evaluated the existence of overhanging medial tibial condyle where the medial eminence line, the line including the medial tibial eminence parallel to the tibial axis, passes outside of the tibial shaft. In all component alignments, patients with a medial overhanging condyle had significantly shorter posterior KCD than those without. In patients with a medial overhanging condyle, the posterior KCD significantly increased when the tibial component was placed in 3° varus (4.6 ± 1.5 mm, P = 0.003 vs neutral, P < 0.001 vs 3° valgus) and 6° varus (5.0 ± 1.4 mm, P < 0.001 vs neutral, P < 0.001 vs 3° valgus) compared with in neutral (3.5 ± 1.9 mm) or 3° valgus (2.8 ± 1.8 mm). In OUKA, varus implantation increased the KCD. This could potentially decrease the risk of fracture, even in knees with the overhanging medial condyle. Conversely, valgus implantation of the tibial component shortened the KCD, and should therefore be avoided.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Short distance from the keel to the posterior tibial cortex is associated with fracture after cementless Oxford UKA in Asian patients.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Apr;30(4):1220-1230. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06553-4. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 33825909
-
Varus placement of the tibial component of Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty decreases the risk of postoperative tibial fracture.Bone Joint J. 2022 Oct;104-B(10):1118-1125. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.104B10.BJJ-2021-1508.R2. Bone Joint J. 2022. PMID: 36177640
-
Varus/valgus angle of the femoral component relative to the tibial component increases risk of bearing dislocation in medial mobile bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jan 20;26(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08292-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 39833818 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in medial knee compartmental osteoarthritis].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 15;35(6):781-785. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202101028. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34142508 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Component placement accuracy in two generations of handheld robotics-assisted knee arthroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021 Dec;141(12):2059-2067. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-04040-6. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021. PMID: 34304279 Review.
Cited by
-
[Successful medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty-What are the most important surgical tricks?].Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2024 Apr;53(4):265-274. doi: 10.1007/s00132-024-04479-6. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38441567 Review. German.
-
Valgus positioning of the femoral component does not compromise short-term clinical outcomes in fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025 Apr 24;35(1):165. doi: 10.1007/s00590-025-04268-7. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 40274613
-
Factors predicting lower limb alignment after Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 7;14(1):5597. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56285-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38454143 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical factors that contribute to tibial periprosthetic fracture after cementless Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Replacement: a finite element analysis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 4;13:1543792. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1543792. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40256778 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

