Whole-orbit radiomics: machine learning-based multi- and fused- region radiomics signatures for intravenous glucocorticoid response prediction in thyroid eye disease
- PMID: 38218934
- PMCID: PMC10787992
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04792-2
Whole-orbit radiomics: machine learning-based multi- and fused- region radiomics signatures for intravenous glucocorticoid response prediction in thyroid eye disease
Abstract
Background: Radiomics analysis of orbital magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows preliminary potential for intravenous glucocorticoid (IVGC) response prediction of thyroid eye disease (TED). The current region of interest segmentation contains only a single organ as extraocular muscles (EOMs). It would be of great value to consider all orbital soft tissues and construct a better prediction model.
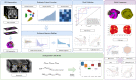
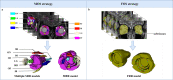
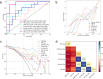
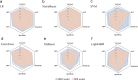
Methods: In this retrospective study, we enrolled 127 patients with TED that received 4·5 g IVGC therapy and had complete follow-up examinations. Pre-treatment orbital T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) was acquired for all subjects. Using multi-organ segmentation (MOS) strategy, we contoured the EOMs, lacrimal gland (LG), orbital fat (OF), and optic nerve (ON), respectively. By fused-organ segmentation (FOS), we contoured the aforementioned structures as a cohesive unit. Whole-orbit radiomics (WOR) models consisting of a multi-regional radiomics (MRR) model and a fused-regional radiomics (FRR) model were further constructed using six machine learning (ML) algorithms.
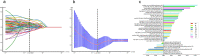
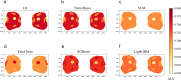
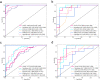
Results: The support vector machine (SVM) classifier had the best performance on the MRR model (AUC = 0·961). The MRR model outperformed the single-regional radiomics (SRR) models (highest AUC = 0·766, XGBoost on EOMs, or LR on OF) and conventional semiquantitative imaging model (highest AUC = 0·760, NaiveBayes). The application of different ML algorithms for the comparison between the MRR model and the FRR model (highest AUC = 0·916, LR) led to different conclusions.
Conclusions: The WOR models achieved a satisfactory result in IVGC response prediction of TED. It would be beneficial to include more orbital structures and implement ML algorithms while constructing radiomics models. The selection of separate or overall segmentation of orbital soft tissues has not yet attained its final optimal result.
Keywords: Intravenous glucocorticoid; MRI; Multi-organ segmentation; Radiomics analysis; Response prediction; Thyroid eye disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential competing interests related to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole-orbit-based multiparametric assessment of disease activity of thyroid eye disease on Dixon MRI.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 May 3;44(1):213. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03138-1. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38700596
-
T2 -Weighted MR Imaging-Derived Radiomics for Pretreatment Determination of Therapeutic Response to Glucocorticoid in Patients With Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy: Comparison With Semiquantitative Evaluation.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Sep;56(3):862-872. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28088. Epub 2022 Jan 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35092642
-
Contrast-enhanced orbital MRI for activity assessment and treatment response prediction in thyroid eye disease.Eur J Radiol. 2025 Jul;188:112136. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2025.112136. Epub 2025 Apr 26. Eur J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40311273
-
Prediction models of intravenous glucocorticoids therapy response in thyroid eye disease.Eur Thyroid J. 2024 Aug 26;13(4):e240122. doi: 10.1530/ETJ-24-0122. Print 2024 Aug 1. Eur Thyroid J. 2024. PMID: 39186944 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Quantitative MRI in Thyroid Eye Disease: Imaging Techniques and Clinical Practices.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Sep;60(3):827-847. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29114. Epub 2023 Nov 16. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37974477 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in artificial intelligence in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 23;15:1356055. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356055. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38715793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-orbit-based multiparametric assessment of disease activity of thyroid eye disease on Dixon MRI.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 May 3;44(1):213. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03138-1. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38700596
-
Integrating ocular and clinical features to enhance intravenous glucocorticoid response prediction in thyroid eye disease: a machine learning approach.Endocrine. 2025 Jun 23. doi: 10.1007/s12020-025-04300-0. Online ahead of print. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 40549141
References
-
- Oculoplastic and Orbital Disease Group of Chinese Ophthalmological Society of Chinese Medical Association Thyroid group of Chinese society of endocrinology of chinese medical association. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022;58(9):646–68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81930024/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82271122/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20DZ2270800/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai
- 2022ZZ01003/Shanghai Key Clinical Specialty, Shanghai Eye Disease Research Center
- JYLJ202202/Clinical Acceleration Program of Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

