Identifying a stable and generalizable factor structure of major depressive disorder across three large longitudinal cohorts
- PMID: 38219346
- PMCID: PMC12165323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2023.115702
Identifying a stable and generalizable factor structure of major depressive disorder across three large longitudinal cohorts
Abstract
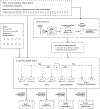
The Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) is the current standard outpatient screening tool for measuring and tracking the nine symptoms of major depressive disorder (MDD). While the PHQ-9 was originally conceptualized as a unidimensional measure, it has become clear that MDD is not a monolithic construct, as evidenced by high comorbidities with other theoretically distinct diagnoses and common symptom overlap between depression and other diagnoses. Therefore, identifying reliable and temporally stable subfactors of depressive symptoms could allow research and care to be tailored to different depression phenotypes. This study improved on previous factor analysis studies of the PHQ-9 by leveraging samples that were clinical (participants with depression only), large (N = 1483 depressed individuals in total), longitudinal (up to 5 years), and from three diverse (matching racial distribution of the United States) datasets. By refraining from assuming the number of factors or item loadings a priori, and thus utilizing a solely data-driven approach, we identified a ranked list of best-fitting models, with the parsimonious one achieving good model fit across studies at most timepoints (average TLI >= 0.90). This model categorizes the PHQ-9 items into four factors: (1) Affective (Anhedonia + Depressed Mood), (2) Somatic (Sleep + Fatigue + Appetite), (3) Internalizing (Worth/Guilt + Suicidality), (4) Sensorimotor (Concentration + Psychomotor), which may be used to further precision psychiatry by testing factor-specific interventions in research and clinical settings.
Keywords: Depression; Factor analysis; PHQ-9; Project baseline health study.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Financial support for this analysis was provided by Verily. Employees of Verily (VWST, JAT, JER, WF, SN) have participated in the conception, analysis, and dissemination of results from this study. PMD has received grants, advisory or board fees and/or stock from several health/biotechnology companies. PMD is an investigator on the PBHS research group and was previously a paid advisor to Verily. PMD is a co-inventor on several patents unrelated to the current manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Arges K, Assimes T, Bajaj V, Balu S, Bashir MR, Beskow L, Blanco R, Califf R, Campbell P, Carin L, Christian V, Cousins S, Das M, Dockery M, Douglas PS, Dunham A, Eckstrand J, Fleischmann D, Ford E, Fraulo E, French J, Gambhir SS, Ginsburg GS, Green RC, Wong CA, 2020. The Project Baseline Health Study: a step towards a broader mission to map human health. NPJ Digital Med. 3, 84. 10.1038/s41746-020-0290-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartlett MS, 1954. A note on the multiplying factors for various χ2 approximations. J. R. Stat. Soc. B-Methodol. 16, 296–298. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1954.tb00174.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources