The putative RNA helicase DDX1 associates with the nuclear RNA exosome and modulates RNA/DNA hybrids (R-loops)
- PMID: 38219817
- PMCID: PMC10875230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105646
The putative RNA helicase DDX1 associates with the nuclear RNA exosome and modulates RNA/DNA hybrids (R-loops)
Abstract
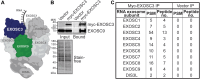
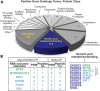
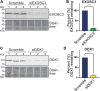
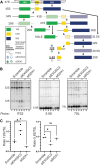
The RNA exosome is a ribonuclease complex that mediates both RNA processing and degradation. This complex is evolutionarily conserved, ubiquitously expressed, and required for fundamental cellular functions, including rRNA processing. The RNA exosome plays roles in regulating gene expression and protecting the genome, including modulating the accumulation of RNA-DNA hybrids (R-loops). The function of the RNA exosome is facilitated by cofactors, such as the RNA helicase MTR4, which binds/remodels RNAs. Recently, missense mutations in RNA exosome subunit genes have been linked to neurological diseases. One possibility to explain why missense mutations in genes encoding RNA exosome subunits lead to neurological diseases is that the complex may interact with cell- or tissue-specific cofactors that are impacted by these changes. To begin addressing this question, we performed immunoprecipitation of the RNA exosome subunit, EXOSC3, in a neuronal cell line (N2A), followed by proteomic analyses to identify novel interactors. We identified the putative RNA helicase, DDX1, as an interactor. DDX1 plays roles in double-strand break repair, rRNA processing, and R-loop modulation. To explore the functional connections between EXOSC3 and DDX1, we examined the interaction following double-strand breaks and analyzed changes in R-loops in N2A cells depleted for EXOSC3 or DDX1 by DNA/RNA immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing. We find that EXOSC3 interaction with DDX1 is decreased in the presence of DNA damage and that loss of EXOSC3 or DDX1 alters R-loops. These results suggest EXOSC3 and DDX1 interact during events of cellular homeostasis and potentially suppress unscrupulous expression of genes promoting neuronal projection.
Keywords: DDX1; DRIP sequencing; R-loop; RNA degradation; RNA exosome; RNA helicase; RNA processing; RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest within the contents of this article.
Figures




Update of
-
The RNA helicase DDX1 associates with the nuclear RNA exosome and modulates R-loops.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 17:2023.04.17.537228. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.17.537228. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2024 Feb;300(2):105646. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105646. PMID: 37131662 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Mitchell P., Petfalski E., Tollervey D. The 3′ end of yeast 5.8S rRNA is generated by an exonuclease processing mechanism. Genes Dev. 1996;10:502–513. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P., Petfalski E., Shevchenko A., Mann M., Tollervey D. The exosome: a conserved eukaryotic RNA processing complex containing multiple 3′-->5′ exoribonucleases. Cell. 1997;91:457–466. - PubMed
-
- Makino D.L., Baumgärtner M., Conti E. Crystal structure of an RNA-bound 11-subunit eukaryotic exosome complex. Nature. 2013;495:70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

