Emerging roles of exosomes in oral diseases progression
- PMID: 38221571
- PMCID: PMC10788352
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-023-00274-9
Emerging roles of exosomes in oral diseases progression
Abstract
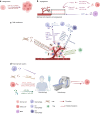
Oral diseases, such as periodontitis, salivary gland diseases, and oral cancers, significantly challenge health conditions due to their detrimental effects on patient's digestive functions, pronunciation, and esthetic demands. Delayed diagnosis and non-targeted treatment profoundly influence patients' prognosis and quality of life. The exploration of innovative approaches for early detection and precise treatment represents a promising frontier in oral medicine. Exosomes, which are characterized as nanometer-sized extracellular vesicles, are secreted by virtually all types of cells. As the research continues, the complex roles of these intracellular-derived extracellular vesicles in biological processes have gradually unfolded. Exosomes have attracted attention as valuable diagnostic and therapeutic tools for their ability to transfer abundant biological cargos and their intricate involvement in multiple cellular functions. In this review, we provide an overview of the recent applications of exosomes within the field of oral diseases, focusing on inflammation-related bone diseases and oral squamous cell carcinomas. We characterize the exosome alterations and demonstrate their potential applications as biomarkers for early diagnosis, highlighting their roles as indicators in multiple oral diseases. We also summarize the promising applications of exosomes in targeted therapy and proposed future directions for the use of exosomes in clinical treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Peres MA, et al. Oral diseases: a global public health challenge. Lancet. 2019;394:249–260. - PubMed
-
- Cheng L, Hill AF. Therapeutically harnessing extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022;21:379–399. - PubMed
-
- Cocucci E, Meldolesi J. Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25:364–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

