Mapping Short Warwick and Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale (SWEMWBS) to Recovering Quality of Life (ReQoL) to estimate health utilities
- PMID: 38221610
- PMCID: PMC10789009
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-023-02220-z
Mapping Short Warwick and Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale (SWEMWBS) to Recovering Quality of Life (ReQoL) to estimate health utilities
Abstract
Background: The Short Warwick and Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale (SWEMWBS) is a widely used non-preference-based measure of mental health in the UK. The primary aim of this paper is to construct an algorithm to translate the SWEMWBS scores to utilities using the Recovering Quality of Life Utility Index (ReQoL-UI) measure.
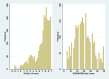
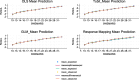
Methods: Service users experiencing mental health difficulties were recruited in two separate cross-sectional studies in the UK. The following direct mapping functions were used: Ordinary Least Square, Tobit, Generalised Linear Models. Indirect (response) mapping was performed using seemingly unrelated ordered probit to predict responses to each of the ReQoL-UI items and subsequently to predict using UK tariffs of the ReQoL-UI from SWEMWBS. The performance of all models was assessed by the mean absolute errors, root mean square errors between the predicted and observed utilities and graphical representations across the SWEMWBS score range.
Results: Analyses were based on 2573 respondents who had complete data on the ReQoL-UI items, SWEMWBS items, age and sex. The direct mapping methods predicted ReQoL-UI scores across the range of SWEMWBS scores reasonably well. Very little differences were found among the three regression specifications in terms of model fit and visual inspection when comparing modelled and actual utility values across the score range of the SWEMWBS. However, when running simulations to consider uncertainty, it is clear that response mapping is superior.
Conclusions: This study presents mapping algorithms from SWEMWBS to ReQoL as an alternative way to generate utilities from SWEMWBS. The algorithm from the indirect mapping is recommended to predict utilities from the SWEMWBS.
Keywords: Mapping; Preference-based measure; QALYs; ReQoL; SWEMWBS.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Estimating a Preference-Based Index for Mental Health From the Recovering Quality of Life Measure: Valuation of Recovering Quality of Life Utility Index.Value Health. 2021 Feb;24(2):281-290. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2020.10.012. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Value Health. 2021. PMID: 33518035 Free PMC article.
-
Enabling QALY estimation in mental health trials and care settings: mapping from the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 to the ReQoL-UI or EQ-5D-5L using mixture models.Qual Life Res. 2023 Oct;32(10):2763-2778. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03443-9. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Qual Life Res. 2023. PMID: 37314661 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating Cost-Effectiveness Using Alternative Preference-Based Scores and Within-Trial Methods: Exploring the Dynamics of the Quality-Adjusted Life-Year Using the EQ-5D 5-Level Version and Recovering Quality of Life Utility Index.Value Health. 2022 Jun;25(6):1018-1029. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2021.11.1358. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Value Health. 2022. PMID: 35667775 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluating and establishing national norms for mental wellbeing using the short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS): findings from the Health Survey for England.Qual Life Res. 2017 May;26(5):1129-1144. doi: 10.1007/s11136-016-1454-8. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Qual Life Res. 2017. PMID: 27853963 Free PMC article.
-
Derivation of a UK preference-based value set for the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS) to allow estimation of Mental Well-being Adjusted Life Years (MWALYs).Soc Sci Med. 2023 Jun;327:115928. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2023.115928. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Soc Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 37201343
Cited by
-
Converting PROMIS®-29 v2.0 profile data to SF-36 physical and mental component summary scores in patients with cardiovascular disorders.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2024 Aug 15;22(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12955-024-02277-4. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2024. PMID: 39148105 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of AIMS: A 4-Week Recovery Oriented Suicide Prevention Pathway.Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2025 Jun;34(3):e70080. doi: 10.1111/inm.70080. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40525708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hurst L, Mahtani K, Pluddemann A, Lewis S, Harvey K, Briggs A, et al. Defining value-based healthcare in the NHS: CEBM report. 2019. Available at: https://046.medsci.ox.ac.uk/files/reports/defining-value-based-healthcar.... Accessed 22 Jan 2023.
-
- Stewart-Brown S, Tennant A, Tennant R, Platt S, Parkinson J, Weich S. Internal construct validity of the Warwick-Edinburgh mental well-being scale (WEMWBS): a Rasch analysis using data from the Scottish health education population survey. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2009;7:1. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-7-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fat LN, Scholes S, Boniface S, Mindell J, Stewart-Brown S. Evaluating and establishing national norms for mental wellbeing using the short Warwick–Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS): findings from the Health Survey for England. Qual Life Res. 2017;26:1129–1144. doi: 10.1007/s11136-016-1454-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

