Vicarious defeat stress induces increased alcohol consumption in female mice: Role of neurokinin-1 receptor and interleukin-6
- PMID: 38221805
- PMCID: PMC10794032
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13357
Vicarious defeat stress induces increased alcohol consumption in female mice: Role of neurokinin-1 receptor and interleukin-6
Abstract
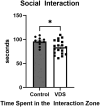
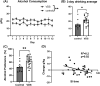
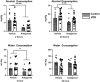
There is a high frequency of comorbidity of alcohol use disorder (AUD) and depression in human populations. We have studied this relationship in our lab using the social defeat stress (SDS) model, which results in both depression-like behaviours and increased alcohol consumption in male mice. However, standard SDS procedures are difficult to use in female mice due to a lack of territorial aggression. In the experiments presented here, we used vicarious defeat stress (VDS) to assess social withdrawal and alcohol consumption in female C57BL6/J mice. We also assessed the expression of interleukin-6 (IL6), which is a proinflammatory cytokine that is associated with depression in humans and sensitivity to SDS in mice. In these experiments, C57BL/6 female mice underwent 10 days of VDS where they witnessed the physical defeat of a male conspecific by an aggressive CD1 mouse. After the end of VDS, mice were either given access to alcohol or sacrificed for the measurement of IL6 expression. We found that VDS increased alcohol consumption and IL6 expression in the frontal cortex and hippocampus. Given that the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) can mediate both stress-induced alcohol consumption and IL6 expression, we tested the ability of NK1R antagonism to reduce VDS-induced alcohol consumption and found that this treatment reduced alcohol intake in both VDS-exposed mice and in unstressed controls. The observed increase in alcohol consumption suggests that VDS is a model that can be utilized to study stress-induced alcohol consumption in female mice, and that this is sensitive to NK1R antagonism.
Keywords: alcohol; neurokinin; stress.
© 2023 The Authors. Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neurokinin-1 receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell influence sensitivity to social defeat stress and stress-induced alcohol consumption in male mice.Addict Neurosci. 2024 Dec;13:100174. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2024.100174. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Addict Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39801674 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional relationship between alcohol intake and sensitivity to social defeat: association with Tacr1 and Avp expression.Addict Biol. 2018 Jan;23(1):142-153. doi: 10.1111/adb.12494. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Addict Biol. 2018. PMID: 28150369 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of lipopolysaccharide exposure on social interaction, cytokine expression, and alcohol consumption in male and female mice.Physiol Behav. 2023 Jun 1;265:114159. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2023.114159. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Physiol Behav. 2023. PMID: 36931488 Free PMC article.
-
Can I Get a Witness? Using Vicarious Defeat Stress to Study Mood-Related Illnesses in Traditionally Understudied Populations.Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Sep 1;88(5):381-391. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.02.004. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32228871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurokinin receptors in drug and alcohol addiction.Brain Res. 2020 May 1;1734:146729. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146729. Epub 2020 Feb 15. Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32067964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurokinin-1 receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell influence sensitivity to social defeat stress and stress-induced alcohol consumption in male mice.Addict Neurosci. 2024 Dec;13:100174. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2024.100174. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Addict Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39801674 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal Viral-Mediated Urokinase Plasminogen Activator (uPA) Overexpression Mitigates Stress-Induced Anxiety and Depression in Rats by Increasing Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 15;14(12):1603. doi: 10.3390/biom14121603. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766310 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation-A Crucial Factor in the Pathophysiology of Depression-A Comprehensive Review.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 30;15(4):502. doi: 10.3390/biom15040502. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

