Hepatic vagotomy blunts liver regeneration after hepatectomy by downregulating the expression of interleukin-22
- PMID: 38222006
- PMCID: PMC10784834
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2866
Hepatic vagotomy blunts liver regeneration after hepatectomy by downregulating the expression of interleukin-22
Abstract
Background: Rapid regeneration of the residual liver is one of the key determinants of successful partial hepatectomy (PHx). At present, there is a lack of recognized safe, effective, and stable drugs to promote liver regeneration. It has been reported that vagus nerve signaling is beneficial to liver regeneration, but the potential mechanism at play here is not fully understood.
Aim: To explore the effect and mechanism of hepatic vagus nerve in liver regeneration after PHx.
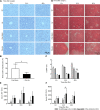
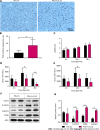
Methods: A PHx plus hepatic vagotomy (Hv) mouse model was established. The effect of Hv on liver regeneration after PHx was determined by comparing the liver regeneration levels of the PHx-Hv group and the PHx-sham group mice. In order to further investigate the role of interleukin (IL)-22 in liver regeneration inhibition mediated by Hv, the levels of IL-22 in the PHx-Hv group and the PHx-sham group was measured. The degree of liver injury in the PHx-Hv group and the PHx-sham group mice was detected to determine the role of the hepatic vagus nerve in liver injury after PHx.
Results: Compared to control-group mice, Hv mice showed severe liver injury and weakened liver regeneration after PHx. Further research found that Hv downregulates the production of IL-22 induced by PHx and blocks activation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway then reduces the expression of various mitogenic and anti-apoptotic proteins after PHx. Exogenous IL-22 reverses the inhibition of liver regeneration induced by Hv and alleviates liver injury, while treatment with IL-22 binding protein (an inhibitor of IL-22 signaling) reduce the concentration of IL-22 induced by PHx, inhibits the activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway in the liver after PHx, thereby hindering liver regeneration and aggravating liver injury in PHx-sham mice.
Conclusion: Hv attenuates liver regeneration after hepatectomy, and the mechanism may be related to the fact that Hv downregulates the production of IL-22, then blocks activation of the STAT3 pathway.
Keywords: Hepatic vagotomy; Interleukin-22; Interleukin-22 binding protein; Liver regeneration; Partial hepatectomy; Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Vagus-macrophage-hepatocyte link promotes post-injury liver regeneration and whole-body survival through hepatic FoxM1 activation.Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 13;9(1):5300. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07747-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30546054 Free PMC article.
-
Netrin-1 promotes liver regeneration possibly by facilitating vagal nerve repair after partial hepatectomy in mice.Cell Signal. 2022 Mar;91:110227. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110227. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 34954393
-
Myeloid peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α deficiency accelerates liver regeneration via IL-6/STAT3 pathway after 2/3 partial hepatectomy in mice.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022 Apr;11(2):199-211. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-20-688. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35464270 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 Trans-signaling Controls Liver Regeneration After Partial Hepatectomy.Hepatology. 2019 Dec;70(6):2075-2091. doi: 10.1002/hep.30774. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 31100194
-
Enhanced Regeneration and Hepatoprotective Effects of Interleukin 22 Fusion Protein on a Predamaged Liver Undergoing Partial Hepatectomy.J Immunol Res. 2018 Oct 31;2018:5241526. doi: 10.1155/2018/5241526. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30515423 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on postoperative liver function in patients undergoing partial hepatectomy: a study protocol for a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 12;12:1603543. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1603543. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40873804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang L, Ma XJ, Fei YY, Han HT, Xu J, Cheng L, Li X. Stem cell therapy in liver regeneration: Focus on mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;232:108004. - PubMed
-
- Ibrahim S, Weiss TS. Augmenter of liver regeneration: Essential for growth and beyond. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;45:65–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

