Deep molecular learning of transcriptional control of a synthetic CRE enhancer and its variants
- PMID: 38222110
- PMCID: PMC10784702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108747
Deep molecular learning of transcriptional control of a synthetic CRE enhancer and its variants
Abstract
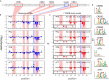
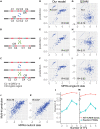
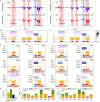
Massively parallel reporter assay measures transcriptional activities of various cis-regulatory modules (CRMs) in a single experiment. We developed a thermodynamic computational model framework that calculates quantitative levels of gene expression directly from regulatory DNA sequences. Using the framework, we investigated the molecular mechanisms of cis-regulatory mutations of a synthetic enhancer that cause abnormal gene expression. We found that, in a human cell line, competitive binding between family transcription factors (TFs) with slightly different binding preferences significantly increases the accuracy of recapitulating the transcriptional effects of thousands of single- or multi-mutations. We also discovered that even if various harmful mutations occurred in an activator binding site, CRM could stably maintain or even increase gene expression through a certain form of competitive binding between family TFs. These findings enhance understanding the effect of SNPs and indels on CRMs and would help building robust custom-designed CRMs for biologics production and gene therapy.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Experimental models in systems biology; Molecular mechanism of gene regulation.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Patent application has been filed by Handong Global University related to this work (Korea Patent application number 10-2023-0049847).
Figures



Similar articles
-
cisMEP: an integrated repository of genomic epigenetic profiles and cis-regulatory modules in Drosophila.BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S8. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S8. Epub 2014 Dec 8. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25521507 Free PMC article.
-
regCNN: identifying Drosophila genome-wide cis-regulatory modules via integrating the local patterns in epigenetic marks and transcription factor binding motifs.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Dec 18;20:296-308. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.12.015. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 35035784 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic and genomic regulatory elements reveal aspects of cis-regulatory grammar in mouse embryonic stem cells.Elife. 2020 Feb 11;9:e41279. doi: 10.7554/eLife.41279. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32043966 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer evolution in chordates: Lessons from functional analyses of cephalochordate cis-regulatory modules.Dev Growth Differ. 2020 Jun;62(5):279-300. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12684. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Dev Growth Differ. 2020. PMID: 32479656 Review.
-
Organizing combinatorial transcription factor recruitment at cis-regulatory modules.Transcription. 2018;9(4):233-239. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1394424. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Transcription. 2018. PMID: 29105538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

