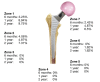A Radiographic Evaluation of Uncemented Total Hip Replacements and the Role of Uncemented Implants in the Management of Hip Osteoarthritis in the Elderly Population
- PMID: 38222132
- PMCID: PMC10787170
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.50487
A Radiographic Evaluation of Uncemented Total Hip Replacements and the Role of Uncemented Implants in the Management of Hip Osteoarthritis in the Elderly Population
Abstract
Introduction The idea of an uncemented, fully coated hydroxyapatite (HA) stem was introduced almost 40 years ago, aiming to achieve a solid biological fixation by preserving natural bone activity. While many studies underline the longevity of uncemented total hip replacement (THR), NHS England's Best Practice Tariff (BPT) recommends using cemented implants in patients over the age of 69, with financial penalties when this policy is not met. At the same time, the 'paradox' of increased use of uncemented implants worldwide has been well described, with many surgeons using them regardless of the age group of the patient. Materials and methods This study focuses on the radiographic evaluation of the uncemented Pinnacle/Corail total hip replacement construct in 123 patients of all age groups who underwent an elective procedure, with a minimum radiographic follow-up of two years. Implant information (collared or non-collared stem), femur type (Dorr classification), age, gender, and revision rate were collected and radiographic analysis of the femoral stem and acetabular component was performed for the immediate post-operative, six-month, one- to two-year follow-up radiograph of all patients. We conducted a statistical analysis, dividing the patients into two groups based on age: those above or below 69 years old. Results There was no statistically significant difference in rates of radiographic lucency after two years with regard to the femoral component. Both collared and non-collared stems seem to perform equally well, with no significant difference detected. However, a statistically significant difference in rates of radiographic lucency of the acetabular cup was noted between the two age groups (p=0.018), with higher rates detected in the under-69-year-old age group. Conclusion This study demonstrates that, radiographically, the uncemented Pinnacle/Corail construct performs equally well in all age groups. In our cohort of patients, the age of the patient did not predict the osseointegration of the implant in the short-term follow-up.
Keywords: cementless total hip arthroplasty; primary hip replacement; total hip arthroplasty: tha; total hip replacement (thr); uncemented hip replacement.
Copyright © 2023, Saraglis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Replacement of arthritic hips by the McKee-Farrar prosthesis. McKee GK, Watson-Farrar J. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5937593/ J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966;48:245–259. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous