External Validation of COOL-AF Scores in the Asian Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Atrial Fibrillation Registry
- PMID: 38222252
- PMCID: PMC10782403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2023.09.011
External Validation of COOL-AF Scores in the Asian Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Atrial Fibrillation Registry
Abstract
Background: The COOL-AF (Cohort of Antithrombotic Use and Optimal International Normalized Ratio Levels in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation) risk scores for death, bleeding, and thromboembolic events (TEs) were derived from the COOL-AF cohort from Thailand and require external validation.
Objectives: The authors sought to externally validate the COOL-AF scores in the APHRS (Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society) registry and to compare their performance in the ESC-EHRA (European Society of Cardiology-European Heart Rhythm Association) EORP-AF (EURObservational Research Programme in Atrial Fibrillation) General Long-Term Registry.
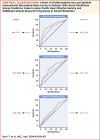
Methods: We studied 3,628 APHRS and 8,825 EORP-AF patients. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and Cox regression analyses were used to test the predictive value of COOL-AF scores and to compared them with the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores.
Results: Patients in the EORP-AF were older, had a higher prevalence of male sex, and were at higher thromboembolic and hemorrhagic risk than APHRS patients. After 1 year of follow-up in APHRS and EORP-AF, the following events were recorded: 87 (2.4%) and 435 (4.9%) death for any causes, 37 (1.0%) and 111 (1.3%) major bleeding, and 25 (0.7%) and 109 (1.2%) TEs, respectively. In APHRS, the COOL-AF scores showed moderate-to-good predictive value for all-cause mortality (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.77; 95% CI: 0.71-0.83), major bleeding (AUC: 0.68; 95% CI: 0.60-0.76), and TEs (AUC: 0.61; 95% CI: 0.51-0.71), and were similar to the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores. In EORP-AF, the predictive value of COOL-AF for all-cause mortality (AUC: 0.68; 95% CI: 0.65-0.70) and major bleeding (AUC: 0.61; 95% CI: 0.60-0.62) was modest and lower than in APHRS. In EORP-AF, the COOL-AF score for TE was inferior to the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
Conclusions: The COOL-AF risk scores may be an easy tool to identify Asian patients with AF at risk for death and major bleeding and performs better in Asian than in European patients with AF. (Clinical Survey on the Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation in Asia [AF-Registry]; NCT04807049).
Keywords: Asians; atrial fibrillation; bleeding; mortality; thromboembolism.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Romiti has done consultancy for Boehringer Ingelheim and has received an educational grant from Anthos, outside the submitted work; no fees are directly received personally. Dr Shimizu has received grants from Daiichi Sankyo Co, Ltd and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co, Ltd; and remuneration for lectures, presentations, Speakers Bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Daiichi Sankyo Co, Ltd, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co, Ltd, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, KK; Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd, Pfizer Japan, Inc, Ono Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, and Medtronic Japan Co, Ltd. Dr Boriani has received small speaker fees from Boston Scientific, Bayer, Boehringer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Dr Lip is a consultant and speaker for BMS/Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Anthos, and Daiichi Sankyo Co, Ltd; no fees were received personally. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures



Comment in
-
Unveiling the Potential of COOL-AF Scores in Diverse Populations: Insights From External Validation.JACC Asia. 2024 Jan 2;4(1):70-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2023.11.002. eCollection 2024 Jan. JACC Asia. 2024. PMID: 39233791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lip G.Y., Nieuwlaat R., Pisters R., Lane D.A., Crijns H.J. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the Euro Heart Survey on Atrial Fibrillation. Chest. 2010;137:263–272. - PubMed
-
- Pisters R., Lane D.A., Nieuwlaat R., de Vos C.B., Crijns H.J., Lip G.Y. A novel user-friendly score (HAS-BLED) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: the Euro Heart Survey. Chest. 2010;138:1093–1100. - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G., Potpara T., Dagres N., et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the task force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

