Yanghe Pingchuan granules mitigates oxidative stress and inflammation in a bronchial asthma rat model: role of the IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling pathway
- PMID: 38222706
- PMCID: PMC10783385
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001553
Yanghe Pingchuan granules mitigates oxidative stress and inflammation in a bronchial asthma rat model: role of the IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling pathway
Abstract
Background: Bronchial asthma (BA) is a chronic inflammatory airway disease. Previous research has shown that Yanghe Pingchuan granules (YPG), among the granules formulated by the First Affiliated Hospital of the Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, exerts a precise therapeutic effect on BA. We previously showed that YPG improves airway inflammation in BA rats. Other studies have shown that the inhibitor of kappa-B kinase (IKK)/inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB)/nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signalling pathway plays a key role in inflammation mediation. Therefore, this study explored whether YPG could intervene in BA through the IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling pathway.
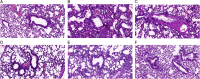
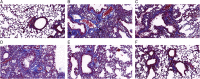
Methods: Ovalbumin-induced method was used to established BA rat model. After successful modelling, the authors used YPG to intervene the rats in BA rats. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was used to detect the bronchial pathological changes in BA rats, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the changes of inflammatory factors (IL-1β and IL-6) and oxidative stress indexes malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and nitrogen monoxide (NO), Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reactionCR and western blot were used to detect the expression of IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling pathway.
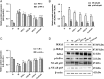
Results: In BA model rats, YPG significantly improved the inflammatory response in bronchial tissues, reduced inflammatory factors IL-1β and IL-6, alleviated oxidative stress, reduced MDA and NO, and increased SOD. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot results showed that YPG could block the IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling pathway.
Conclusion: These findings showed that YPG had a definite therapeutic effect on BA, which may be related to blocking the IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling pathway and improving inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling pathway; Yanghe Pingchuan granules; bronchial asthma; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
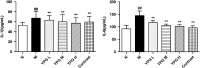
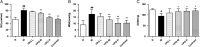
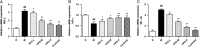
Similar articles
-
Yanghe Pingchuan Granules Alleviate Airway Inflammation in Bronchial Asthma and Inhibit Pyroptosis by Blocking the TLR4/NF-κB/NRLP3 Signaling Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Aug 31;2022:6561048. doi: 10.1155/2022/6561048. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 36091667 Free PMC article.
-
Yanghe Pingchuan granules induce ferroptosis in airway smooth muscle cells to improve bronchial asthma via the METTL3/P53/SLC7A11 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2025 Apr;139:156480. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156480. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39978273
-
Mechanism of Yanghe Pingchuan granules treatment for airway remodeling in asthma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Jun 27;12:1941-1951. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S159428. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29983548 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the mechanism of action of Yanghe Pingchuan Granule in the treatment of bronchial asthma based on bioinformatics and experimental validation.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 2;9(11):e21936. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21936. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027735 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and radical-induced signalling.In: Baan RA, Stewart BW, Straif K, editors. Tumour Site Concordance and Mechanisms of Carcinogenesis. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2019. Chapter 15. In: Baan RA, Stewart BW, Straif K, editors. Tumour Site Concordance and Mechanisms of Carcinogenesis. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2019. Chapter 15. PMID: 33979089 Free Books & Documents. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Liu JX, Zhang Y, Yuan HY, et al. . The treatment of asthma using the Chinese Materia Medica. J Ethnopharmacol 2021;269:113558. - PubMed
-
- Beasley R, Weatherall M. The vexed problem of corticosteroid toxicity in asthma: time for standardized assessment. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021;9:373–374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
