Establishment of models to predict factors influencing periodontitis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 38222787
- PMCID: PMC10784791
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1793
Establishment of models to predict factors influencing periodontitis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with periodontitis. Currently, there are few studies proposing predictive models for periodontitis in patients with T2DM.
Aim: To determine the factors influencing periodontitis in patients with T2DM by constructing logistic regression and random forest models.
Methods: In this a retrospective study, 300 patients with T2DM who were hospitalized at the First People's Hospital of Wenling from January 2022 to June 2022 were selected for inclusion, and their data were collected from hospital records. We used logistic regression to analyze factors associated with periodontitis in patients with T2DM, and random forest and logistic regression prediction models were established. The prediction efficiency of the models was compared using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
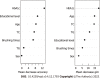
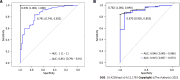
Results: Of 300 patients with T2DM, 224 had periodontitis, with an incidence of 74.67%. Logistic regression analysis showed that age [odds ratio (OR) = 1.047, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.017-1.078], teeth brushing frequency (OR = 4.303, 95%CI: 2.154-8.599), education level (OR = 0.528, 95%CI: 0.348-0.800), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (OR = 2.545, 95%CI: 1.770-3.661), total cholesterol (TC) (OR = 2.872, 95%CI: 1.725-4.781), and triglyceride (TG) (OR = 3.306, 95%CI: 1.019-10.723) influenced the occurrence of periodontitis (P < 0.05). The random forest model showed that the most influential variable was HbA1c followed by age, TC, TG, education level, brushing frequency, and sex. Comparison of the prediction effects of the two models showed that in the training dataset, the AUC of the random forest model was higher than that of the logistic regression model (AUC = 1.000 vs AUC = 0.851; P < 0.05). In the validation dataset, there was no significant difference in AUC between the random forest and logistic regression models (AUC = 0.946 vs AUC = 0.915; P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Both random forest and logistic regression models have good predictive value and can accurately predict the risk of periodontitis in patients with T2DM.
Keywords: Gingival disease; Logistic regression; Periodontitis; Prediction model; Random forest model; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Periodontitis: An often-neglected complication of diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2024 Mar 15;15(3):318-325. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.318. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38591080 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical study of different prediction models in predicting diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jan 15;15(1):43-52. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i1.43. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38313855 Free PMC article.
-
[Blood Lipid Indicators and Different Clinical Classifications of Dyslipidemia and Diabetic Kidney Disease: Correlation and Predictive Value].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Sep;54(5):1013-1018. doi: 10.12182/20230960103. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37866961 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Predicting the risk of subclinical atherosclerosis based on interpretable machine models in a Chinese T2DM population.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 27;15:1332982. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1332982. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38476673 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram Prediction for the Risk of Diabetic Foot in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 13;13:890057. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.890057. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35909507 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Prediction Model for External Root Resorption of the Second Molars Associated With Third Molars.Int Dent J. 2025 Feb;75(1):195-205. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.09.031. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 39472249 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontitis: An often-neglected complication of diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2024 Mar 15;15(3):318-325. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.318. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38591080 Free PMC article.
-
Role of viruses in periodontitis: An extensive review of herpesviruses, human immunodeficiency virus, coronavirus-19, papillomavirus and hepatitis viruses.World J Virol. 2024 Dec 25;13(4):99070. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v13.i4.99070. World J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39722755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Artificial Intelligence-Based Fuzzy Logic System for Periodontitis Risk Assessment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;12(3):211. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12030211. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Genco RJ, Borgnakke WS. Diabetes as a potential risk for periodontitis: association studies. Periodontol 2000. 2020;83:40–45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

