Empagliflozin ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy probably via activating AMPK/PGC-1α and inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK pathway
- PMID: 38222788
- PMCID: PMC10784799
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1862
Empagliflozin ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy probably via activating AMPK/PGC-1α and inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK pathway
Abstract
Background: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) increases the risk of hospitalization for heart failure (HF) and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. However, no specific therapy to delay the progression of DCM has been identified. Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and calcium handling imbalance play a crucial role in the pathological processes of DCM, ultimately leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunctions. Empagliflozin, a novel glucose-lowering agent, has been confirmed to reduce the risk of hospitalization for HF in diabetic patients. Nevertheless, the molecular mechanisms by which this agent provides cardioprotection remain unclear.
Aim: To investigate the effects of empagliflozin on high glucose (HG)-induced oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis and the underlying molecular mechanism.
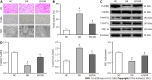
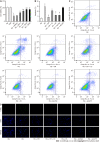
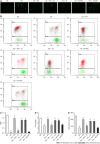
Methods: Twelve-week-old db/db mice and primary cardiomyocytes from neonatal rats stimulated with HG (30 mmol/L) were separately employed as in vivo and in vitro models. Echocardiography was used to evaluate cardiac function. Flow cytometry and TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling staining were used to assess apoptosis in myocardial cells. Mitochondrial function was assessed by cellular ATP levels and changes in mitochondrial membrane potential. Furthermore, intracellular reactive oxygen species production and superoxide dismutase activity were analyzed. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to analyze Bax and Bcl-2 mRNA expression. Western blot analysis was used to measure the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 (MYPT1), as well as the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) and active caspase-3 protein levels.
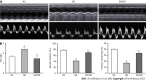
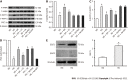
Results: In the in vivo experiment, db/db mice developed DCM. However, the treatment of db/db mice with empagliflozin (10 mg/kg/d) for 8 wk substantially enhanced cardiac function and significantly reduced myocardial apoptosis, accompanied by an increase in the phosphorylation of AMPK and PGC-1α protein levels, as well as a decrease in the phosphorylation of MYPT1 in the heart. In the in vitro experiment, the findings indicate that treatment of cardiomyocytes with empagliflozin (10 μM) or fasudil (FA) (a ROCK inhibitor, 100 μM) or overexpression of PGC-1α significantly attenuated HG-induced mitochondrial injury, oxidative stress, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. However, the above effects were partly reversed by the addition of compound C (CC). In cells exposed to HG, empagliflozin treatment increased the protein levels of p-AMPK and PGC-1α protein while decreasing phosphorylated MYPT1 levels, and these changes were mitigated by the addition of CC. Adding FA and overexpressing PGC-1α in cells exposed to HG substantially increased PGC-1α protein levels. In addition, no sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT)2 protein expression was detected in cardiomyocytes.
Conclusion: Empagliflozin partially achieves anti-oxidative stress and anti-apoptotic effects on cardiomyocytes under HG conditions by activating AMPK/PGC-1α and suppressing of the RhoA/ROCK pathway independent of SGLT2.
Keywords: AMPK; Apoptosis; Diabetic cardiomyopathy; Empagliflozin; Oxidative stress; ROCK.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no competing interests for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CTRP6-mediated cardiac protection in heart failure via the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α signalling pathway.Exp Physiol. 2024 Dec;109(12):2031-2045. doi: 10.1113/EP092036. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39325807 Free PMC article.
-
The RhoA/ROCK pathway mediates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via oxidative stress, JNK, and p38MAPK pathways.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018 Sep;34(6):e3022. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3022. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29745021
-
MALAT1/miR-185-5p mediated high glucose-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial injury and cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the RhoA/ROCK pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Sep;27(17):2495-2506. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17835. Epub 2023 Jul 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37395157 Free PMC article.
-
The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Coactivator-1α-Heme Oxygenase 1 Axis, a Powerful Antioxidative Pathway with Potential to Attenuate Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 Jun 10;32(17):1273-1290. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7989. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020. PMID: 32027164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qiliqiangxin: A multifaceted holistic treatment for heart failure or a pharmacological probe for the identification of cardioprotective mechanisms?Eur J Heart Fail. 2023 Dec;25(12):2130-2143. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.3068. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Eur J Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 37877337 Review.
Cited by
-
The Off-Target Cardioprotective Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 14;25(14):7711. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147711. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Empagliflozin Alleviates Carfilzomib-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice by Modulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Response, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Autophagy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 30;13(6):671. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060671. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929110 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the cardioprotective mechanisms of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors beyond glycemic control.World J Diabetes. 2024 Feb 15;15(2):137-141. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.137. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38464375 Free PMC article.
-
The landscape of novel antidiabetic drugs in diabetic HFpEF: relevant mechanisms and clinical implications.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Apr 28;24(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02750-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40295996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical Appraisal of Pharmaceutical Therapy in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy-Challenges and Prospectives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;18(1):134. doi: 10.3390/ph18010134. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Habotta OA, Abdeen A, Roomi AB, Elgndy AI, Sorour SM, Morsi MH, Kamal KM, Ibrahim SF, Abdelrahaman D, Fericean L, Banatean-Dunea I, Ghamry HI, El-Nablaway M, Atawia RT, Abdelhady D. Nootkatone Mitigated Melamine-Evoked Hepatotoxicity by Featuring Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Interconnected Mechanisms: In Vivo and In Silico Approaches. Toxics. 2023;11 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

