Comparison of artificial intelligence, elastic imaging, and the thyroid imaging reporting and data system in the differential diagnosis of suspicious nodules
- PMID: 38223033
- PMCID: PMC10784040
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-23-788
Comparison of artificial intelligence, elastic imaging, and the thyroid imaging reporting and data system in the differential diagnosis of suspicious nodules
Abstract
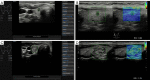
Background: Ultrasound is widely used for detecting thyroid nodules in clinical practice. This retrospective study aimed to assess the diagnostic efficacy of the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (ACR-TIRADS), S-Detect, and elastography of the carotid artery for suspicious thyroid nodules and to determine the complementary value of artificial intelligence and elastography.
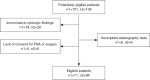
Methods: Between January 2021 and November 2021, 101 consecutive patients with 138 thyroid nodules were enrolled in The First Hospital of China Medical University. All nodules were evaluated using ACR-TIRADS categories (TR), S-Detect, and elastography, and then the diagnostic performance of the different methods and the combined assessment were compared. The inclusion criteria were the following: (I) TR3, TR4, and TR5 nodules, which were defined as "suspicious nodules"; (II) patients who had surgical or cytopathological results after ultrasound examination; and (III) voluntary enrollment in this study. Meanwhile, the exclusion criteria were the following: (I) TR1 and TR2 nodules, (II) patients who had undergone fine-needle aspiration before ultrasound examination, and (III) inconclusive cytologic findings.
Results: A total of 71 patients (12 men and 59 women) with 94 suspicious thyroid nodules (42 benign nodules and 52 malignant nodules) were finally included in this study. S-Detect had a significantly better sensitivity than did ACR-TIRADS [S-Detect: 98.1%, 95% confidence interval (CI): 89.7-100.0%; ACR-TIRADS: 84.6%, 95% CI: 71.9-93.1%; P=0.036], but its specificity was much lower (S-Detect: 19.0%; 95% CI: 8.6-34.1%; ACR-TIRADS: 40.5%, 95% CI: 25.6-56.7%; P=0.032). The accuracy was not significantly different between S-Detect (62.8%; 95% CI: 52.2-72.5%) and ACR-TIRADS (64.9%; 95% CI: 54.4-74.5%) (P=0.761). The elasticity contrast index (ECI) was not definitively useful in identifying suspicious thyroid nodules (P=0.592). Compared with the use of ACR-TIRADS and S-Detect alone, the specificity (45.2%; 95% CI: 29.8-61.3%), positive predictive value (65.2%; 95% CI: 52.4-76.5%), accuracy (66.0%; 95% CI: 55.5-75.4%), and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (0.640; 95% CI: 0.534-0.736) of their combination were higher but not significantly so.
Conclusions: At present, S-Detect cannot replace manual diagnosis, and the value of elastography of the carotid artery in diagnosing suspected thyroid nodules remains unclear.
Keywords: Thyroid nodule; artificial intelligence (AI); elastography; ultrasonography.
2024 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-23-788/coif). Y.F.Z. reports that this work was funded by the Health and Medical Big Data Research Institute of China Medical University (No. HMB201901103). The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
