Prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT tumor metabolic parameters and Ki-67 in pre-treatment diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 38223089
- PMCID: PMC10784016
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-23-702
Prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT tumor metabolic parameters and Ki-67 in pre-treatment diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a highly aggressive lymphoma. Rituximab-based conventional chemotherapy still leads to drug resistance or relapse in 30-40% of patients. Therefore, early identification of high-risk patients and accurate assessment of prognosis are very important for clinical decision-making. The aim of this study is to investigate the value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) of tumor metabolic, clinical and biological parameters in the prognostic risk stratification of DLBCL before treatment.
Methods: We retrospectively collected clinical data on 63 patients with newly diagnosed DLBCL admitted to Shanxi Bethune Hospital during the period from November 2016 to April 2020 who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT prior to treatment in a cohort study. Metabolic, clinical, and biological parameters were analyzed by Cox regression. Kaplan-Meier curves of patient survival were compared by the log-rank test.
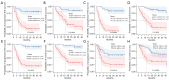
Results: The median follow-up was 21 months. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 47.62%, and the overall survival (OS) was 53.97%. The subtype, double expression, Ann Abor stage, NCCN-IPI score, Ki-67, maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), bulk volume glycolysis (BVG), total lesion glycolysis (TLG), total metabolic tumor volume (TMTV) were the influencing factors for PFS and OS (P<0.050) in univariate analysis. BVG (PFS: HR =6.62, P<0.001; OS: HR =3.53, P=0.029), TLG (PFS: HR =8.56, P<0.001; OS: HR =5.20, P=0.004), TMTV (PFS: HR =12.02, P=0.001; OS: HR =5.05, P=0.033) and Ki-67 were found to be independent prognostic risk stratification parameters affecting PFS and OS by multivariate regression analysis. The 2-year PFS and OS rates for patients with high BVG (≥288.00 cm3), TLG (≥1,854.00 cm3), TMTV (≥103.00 cm3), and Ki-67 (≥85%) were 20% and 28.57%, 9.68% and 22.58%, 20.51%, and 30.77%, and 25% and 33.33%, respectively; and the 2-year PFS and OS rates for patients with low BVG (<288.00 cm3), TLG (<1,854.00 cm3), TMTV (<103.00 cm3), and Ki-67 (<85%) patients were 82.14% and 85.71%, 84.37% and 84.37%, 91.67% and 91.67%, and 61.54% and 66.67%, respectively. Patients with high BVG, TLG, TMTV, and Ki-67 had a worse 2-year PFS as well as OS rate (Ki-67: P=0.0018/P=0.0025; P<0.0001 for the rest of the groups).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that BVG, TLG, TMTV, and Ki-67 are independent prognostic indicators for survival in patients with pre-treatment DLBCL, especially BVG, which is a novel prognostic indicator that has to be validated in future research.
Keywords: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT); Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL); prognosis.
2024 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-23-702/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of metabolic tumour volume on baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT in addition to NCCN-IPI in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: further stratification of the group with a high-risk NCCN-IPI.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Jul;46(7):1417-1427. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04309-4. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30941463
-
A novel prognostic model utilizing TMTV and SUVmax from 18F-FDG PET/CT for predicting overall survival in patients with extranodal NK/T- cell lymphoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 3;25(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13725-9. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40033269 Free PMC article.
-
[18F-FDG PET/CT Metabolic Parameters and Circulating Tumour DNA Mutation Abundance in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Correlation and Survival Analysis].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Dec;31(6):1690-1700. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2023.06.014. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38071047 Chinese.
-
Predictive value of F-18 FDG PET/CT quantization parameters in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis with 702 participants.Med Oncol. 2015 Jan;32(1):446. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0446-1. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25511321
-
Prognostic prediction by 18F-FDG-PET/CT parameters in patients with neuroblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 14;13:1208531. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1208531. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37519817 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correlation of PET/CT Maximal Standardized Uptake Values with Clinicopathologic Parameters of Aggressive Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2025 May 22;17:975-984. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S522628. eCollection 2025. Cancer Manag Res. 2025. PMID: 40432709 Free PMC article.
-
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-compute tomography parameters for predicting the prognosis and toxicity in children and young adults with large B-cell lymphoma receiving chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Mar 3;15(3):2209-2221. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1737. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40160608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J, Zhang R, Ding X, Jin Y, Qin R, Xia B, Liao Q, Hu H, Song W, Wang Z, Zhang X, Xu J. Pathologically complete remission to combination of invariant NK T cells and anti-CD20 antibody in a refractory HIV+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patient. Immunotherapy 2022;14:599-607. 10.2217/imt-2021-0247 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, Klasa R, Savage KJ, Shenkier T, Sutherland J, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 2007;109:1857-61. 10.1182/blood-2006-08-038257 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
