Single source CARS-based multimodal microscopy system for biological tissue imaging [Invited]
- PMID: 38223172
- PMCID: PMC10783911
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.504978
Single source CARS-based multimodal microscopy system for biological tissue imaging [Invited]
Abstract
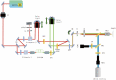
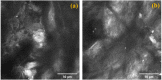
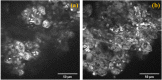
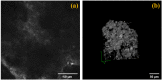
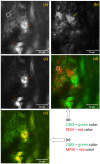
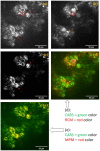
A coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS)-based multimodality microscopy system was developed using a single Ti:sapphire femtosecond laser source for biological imaging. It provides three complementary and co-registered imaging modalities: CARS, MPM (multiphoton microscopy), and RCM (reflectance confocal microscopy). The imaging speed is about 1 frame-per-second (fps) with a digital resolution of 1024 × 1024 pixels. This microscopy system can provide clear 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional images of ex-vivo biological tissue samples. Its spectral selection initiates vibrational excitation in lipid cells (approximately 2850 cm-1) using two filters on the pump and Stokes beam paths. The excitation can be tuned over a wide spectral range with adjustable spectral filters. The imaging capability of this CARS-based multimodal microscopy system was demonstrated using porcine fat, murine skin, and murine liver tissue samples.
© 2023 Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Optica Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous hyperspectral differential-CARS, TPF and SHG microscopy with a single 5 fs Ti:Sa laser.Opt Express. 2013 Mar 25;21(6):7096-106. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.007096. Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 23546091
-
Implementation of a Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering (CARS) System on a Ti:Sapphire and OPO Laser Based Standard Laser Scanning Microscope.J Vis Exp. 2016 Jul 17;(113). doi: 10.3791/54262. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27501285
-
Fast vibrational imaging of single cells and tissues by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Aug 19;47(8):2282-90. doi: 10.1021/ar400331q. Epub 2014 May 28. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24871269 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrally-broad coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering hyper-microscopy utilizing a Stokes supercontinuum pumped at 800 nm.Biomed Opt Express. 2016 Sep 27;7(10):4335-4345. doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.004335. eCollection 2016 Oct 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2016. PMID: 27867735 Free PMC article.
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Techniques in Microscopy: introduction to the feature issue.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Feb 22;15(3):1813-1814. doi: 10.1364/BOE.521511. eCollection 2024 Mar 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 38495684 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Raman and Partial Wave Spectroscopy Microscope for the Characterization of Molecular and Structural Alterations in Tissue.J Biophotonics. 2024 Dec;17(12):e202400330. doi: 10.1002/jbio.202400330. Epub 2024 Oct 27. J Biophotonics. 2024. PMID: 39462506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaiser W., Garrett C. G. B., “Two-photon excitation in CaF2:Eu2+,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 7(6), 229–231 (1961).10.1103/PhysRevLett.7.229 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
