Serum omentin-1 is correlated with the severity of liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 38223417
- PMCID: PMC10784814
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1315
Serum omentin-1 is correlated with the severity of liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: Patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection have increased serum omentin-1. Omentin-1 is an anti-inflammatory adipokine, and higher levels may be a direct effect of HCV infection. Successful elimination of HCV by direct acting antivirals almost normalized circulating levels of various molecules with a role in inflammation.
Aim: To evaluate the effect of HCV infection on serum omentin-1, serum omentin-1 levels of HCV patients were measured before therapy and at 12 wk after therapy end. Associations of serum omentin-1 with parameters of inflammation and liver function were explored at both time points. Serum omentin-1 levels of patients with and without liver cirrhosis, which was defined by ultrasound or the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score, were compared.
Methods: Serum omentin-1 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 84 chronic HCV patients before therapy and at 12 wk after therapy end where sustained virological response 12 (SVR12) was achieved in all patients. Serum omentin-1 of 14 non-infected controls was measured in parallel.
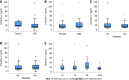
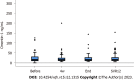
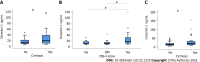
Results: In patients with chronic HCV, serum omentin-1 levels were not related to viral load or viral genotype. HCV patients with liver steatosis and HCV patients with diabetes had serum omentin-1 levels comparable to patients not suffering from these conditions. Serum omentin-1 levels at SVR12 were similar in comparison to pretreatment levels. In addition, serum levels did not differ between HCV-infected patients and non-infected controls. Serum omentin-1 levels did not correlate with leukocyte count or C-reactive protein. Positive correlations of serum omentin-1 with bilirubin and the model for end-stage liver disease score (MELD) were detected before therapy and at SVR12 in the whole cohort. Bilirubin and the MELD score also positively correlated with serum omentin-1 levels in the subgroup of patients with ultrasound diagnosed liver cirrhosis before therapy. At SVR12, serum omentin-1 levels of patients with liver cirrhosis negatively correlated with albumin. Before therapy start, patients with high FIB-4 scores had increased serum omentin-1 in comparison to patients with a low score. Serum omentin-1 levels of patients with liver cirrhosis defined by ultrasound were increased at baseline and at SVR12.
Conclusion: Present study showed that liver cirrhosis, but not HCV infection per se, is related to elevated serum omentin-1 levels.
Keywords: Adipokine; Direct acting antivirals; Hepatitis C; Liver cirrhosis.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Omentin-General Overview of Its Role in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Other Diseases; Problem of Current Research State.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 5;13(3):632. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030632. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Galectin-3 in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Declines after Successful Virus Eradication by Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2022 Dec 17;31(4):444-452. doi: 10.15403/jgld-4341. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2022. PMID: 36535063
-
Gender-Specific Differences in Serum Sphingomyelin Species in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus Infection-Sphingomyelin Species Are Related to the Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score in Male Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 7;24(9):8402. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098402. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176109 Free PMC article.
-
DAA therapy and long-term hepatic function in advanced/decompensated cirrhosis: Real-world experience from HCV-TARGET cohort.J Hepatol. 2020 Sep;73(3):540-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.031. Epub 2020 Mar 31. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32243960 Clinical Trial.
-
Chemerin Is a Valuable Biomarker in Patients with HCV Infection and Correlates with Liver Injury.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Nov 19;10(11):974. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110974. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33228201 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship between serum Midkine and Omentin-1 levels and the severity of sepsis in patients and their prognostic value.Libyan J Med. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):2383025. doi: 10.1080/19932820.2024.2383025. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Libyan J Med. 2024. PMID: 39042809 Free PMC article.
-
Omentin-General Overview of Its Role in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Other Diseases; Problem of Current Research State.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 5;13(3):632. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030632. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Torres M, Poynard T. Risk factors for liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Ann Hepatol. 2003;2:5–11. - PubMed
-
- Hengst J, Falk CS, Schlaphoff V, Deterding K, Manns MP, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H. Direct-Acting Antiviral-Induced Hepatitis C Virus Clearance Does Not Completely Restore the Altered Cytokine and Chemokine Milieu in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C. J Infect Dis. 2016;214:1965–1974. - PubMed
-
- Peschel G, Grimm J, Buechler C, Gunckel M, Pollinger K, Aschenbrenner E, Kammerer S, Jung EM, Haimerl M, Werner J, Müller M, Weigand K. Liver stiffness assessed by shear-wave elastography declines in parallel with immunoregulatory proteins in patients with chronic HCV infection during DAA therapy. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2021;79:541–555. - PubMed
-
- Saraiva GN, do Rosário NF, Medeiros T, Leite PEC, Lacerda GS, de Andrade TG, de Azeredo EL, Ancuta P, Almeida JR, Xavier AR, Silva AA. Restoring Inflammatory Mediator Balance after Sofosbuvir-Induced Viral Clearance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:8578051. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

