PD1 and TIM3 Expression is Associated with Very Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Percutaneous Thermal Ablation
- PMID: 38223553
- PMCID: PMC10787562
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S443134
PD1 and TIM3 Expression is Associated with Very Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Percutaneous Thermal Ablation
Abstract
Purpose: Percutaneous thermal ablation (PTA) is a cornerstone in the management of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, intrahepatic distant recurrence (IDR) occurs in the majority of patients after PTA. The aim of this study was to evaluate the immune signature associated with very early IDR.
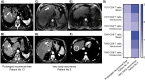
Patients and methods: Thirty-one patients (26 men, 5 women; mean age:72.4 ± 8.6; age range:57-86 years) who underwent PTA for HCC were included in this study. After PTA for HCC, patients were followed and later divided into two groups: a "very early recurrence" group in case of IDR within 12 months after PTA, and a "prolonged recurrence-free" group in case of no recurrence before 12 months of follow-up. Freshly harvested intratumoral and nontumoral liver tissues and peripheral blood were obtained before PTA and explored by multiparametric flow cytometry.
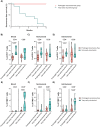
Results: The frequency of PD1+CD4+ T cells was higher in the early recurrence group than in the prolonged recurrence-free group in the peripheral blood (24.3%, IQR: 22.3-36.5 vs 14.0%, IQR: 11.5-16.4, p<0.0001), in the nontumoral liver (37.9%, IQR: 36.0-50.0 vs 22.5%, IQR: 18.0-29.9, p=0.0004), and in the tumor (37.6%, IQR: 32.3-39.3 vs 24.0%, IQR: 20.0-30.3, p=0.0137). Similarly, the frequency of TIM+CD8+ T cells was higher in the very early recurrence group in the peripheral blood (p=0.0021), non-tumoral liver (p=0.0012), and tumor (p=0.0239).
Conclusion: The expression of immune checkpoint molecules, such as PD1 and TIM3 on T cells identified HCC patients at risk of very early IDR after PTA who would likely benefit from adjuvant immunotherapy. Thus, our study contributes to a better understanding of the potential association of PTA with adjuvant immunotherapies.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immune checkpoint molecules; intrahepatic distant recurrence; percutaneous thermal ablation; predictive factors.
© 2024 Ghelfi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Dr. Charlotte Costentin reports grants, personal fees, non-financial support from Gilead, non-financial support from Ipsen, personal fees, non-financial support from AbbVie, RNPC, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Wang H, Wu Z, Cui D, Shi Y, Zhai B. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: current status, challenges, and prospects. Liver Res. 2023;7(2):108–115. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2023.05.002 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

