An Engineered Influenza a Virus Expressing the Co-Stimulator OX40L as an Oncolytic Agent Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 38223555
- PMCID: PMC10787515
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S410703
An Engineered Influenza a Virus Expressing the Co-Stimulator OX40L as an Oncolytic Agent Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Oncolytic virus (OV) therapy has emerged as a promising novel form of immunotherapy. Moreover, an increasing number of studies have shown that the therapeutic efficacy of OV can be further improved by arming OVs with immune-stimulating molecules.
Methods: In this study, we used reverse genetics to produce a novel influenza A virus, termed IAV-OX40L, which contained the immune-stimulating molecule OX40L gene in the influenza virus nonstructural (NS1) protein gene. The oncolytic effect of IAV-OX40L was explored on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)HCC cells in vitro and in vivo.
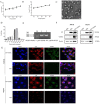
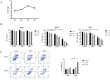
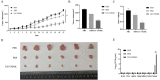
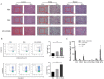
Results: Hemagglutination titers of the IAV-OX40L virus were stably 27-28 in specific-pathogen-free chicken embryos. The morphology and size distribution of IAV-OX40L are similar to those of the wild-type influenza. Expression of OX40L protein was confirmed by Western blot and immunofluorescence. MTS assays showed that the cytotoxicity of IAV-OX40L was higher in HCC cells (HepG2 and Huh7) than in normal liver cells (MIHA) in a time- and dose-dependent manner in vitro. We found that intratumoral injection of IAV-OX40L reduced tumor growth and increased the survival rate of mice compared with PR8-treated controls in vivo. In addition, the pathological results showed that IAV-OX40L selectively destroyed tumor tissues without harming liver and lung tissues. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of the IAV-OX40L group were significantly increased in the splenic lymphocytes of mice. Further validation confirmed that IAV-OX40L enhanced the immune response mainly by activating Th1-dominant immune cells, releasing interferon-γ and interleukin-2.
Conclusion: Taken together, our findings demonstrate the novel chimeric influenza OV could provide a potential therapeutic strategy for combating HCC and improve the effectiveness of virotherapy for cancer therapy.
Keywords: HCC; IAV; OVs; OX40L.
© 2024 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

