Pulmonary artery diameter and NT-proBNP in patients with Covid-19: Predicting prognosis and mortality
- PMID: 38223639
- PMCID: PMC10782310
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v23i2.64
Pulmonary artery diameter and NT-proBNP in patients with Covid-19: Predicting prognosis and mortality
Abstract
Background: The diverse and complex presentations of COVID-19 continue to impact the world. Factors related to prognosis and mortality are still not fully illuminated.
Objectives: We aimed to asses the relationship of N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and main pulmonary artery diameter (MPAD) with COVID-19 prognosis and mortality.
Methods: 152 COVID-19 patients over the age of 18, were included in the study. Thoracic CT, NT-proBNP values, laboratory and demographic data of these patients were obtained by retrospectively examining the patient files and scanning the results through the patient registry.
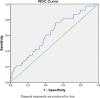
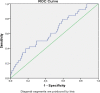
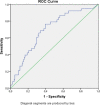
Results: According to multivariate logistic regression (LR) analysis, high NT-proBNP level (OR=3.542; 95% CI=1.745-9.463; p=0.021) and MPAD/ascending aortic diameter (AAD) ratio>0.75 (OR=2.692; 95% CI=1.264-9.312; p=0.036) were determined as independent risk factors predicting mortality in COVID-19 patients. A significant positive correlation was observed between NT-proBNP level and MPA diameter (r=0.296, p<0.001). The cut-off value was measured as 27.5 mm for MPA diameter and 742 pg/ml for NT-proBNP.
Conclusions: Accurate and effective interpretation of available radiological and laboratory data is essential to reveal the factors predicting prognosis and mortality in COVID-19. In this study,we evaluated that the thorax CTs and determined that the MPAD/AAD and NT-proBNP level were independent risk factors in predicting mortality.
Keywords: COVID-19; MPAD/AAD ratio; NT-proBNP; Pulmonary artery diameter.
© 2023 Tastemur M et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Value of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and aortic diameter in predicting in-hospital mortality in acute aortic dissection.Cytokine. 2019 Jul;119:90-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30903868
-
The association of baseline N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide with short and long-term prognosis following percutaneous coronary intervention in non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome with multivessel coronary artery disease: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Apr 21;21(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02010-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 33882836 Free PMC article.
-
Post-procedural N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide predicts one-year mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation.Rev Port Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2018 Jan;37(1):67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2017.06.016. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Rev Port Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 29317115 English, Portuguese.
-
Elevated N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis.Postgrad Med J. 2020 Jul;96(1137):387-391. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-137884. Epub 2020 May 20. Postgrad Med J. 2020. PMID: 32434874 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and short-term mortality in acute aortic dissection: A meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2020 Nov;43(11):1255-1259. doi: 10.1002/clc.23436. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Clin Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32735030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Editor's choice: Covid-19 and HIV are still very much with us.Afr Health Sci. 2023 Jun;23(2):i-v. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i2.1. Afr Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 38223647 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Medicine JHU, author. Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. 2022. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/
-
- Waller JV, Kaur P, Tucker A, Lin KK, Diaz MJ, Henry TS, et al. Diagnostic Tools for Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Comparing CT and RT-PCR Viral Nucleic Acid Testing. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215(4):834–838. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
