Electroacupuncture on Baihui (DU20) and Xuehai (SP10) acupoints alleviates psoriatic inflammation by regulating neurotransmitter substance P- Neurokinin-1 receptor signaling
- PMID: 38223807
- PMCID: PMC10785156
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.07.005
Electroacupuncture on Baihui (DU20) and Xuehai (SP10) acupoints alleviates psoriatic inflammation by regulating neurotransmitter substance P- Neurokinin-1 receptor signaling
Abstract
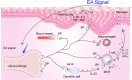
Background: At present, acupuncture-related practices have been widely used to treat psoriasis. In our study, we investigated the effect and explored the mechanism of electroacupuncture (EA) on acupoints Baihui (DU20) and Xuehai (SP10) for the treatment of psoriasis.
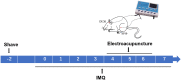
Methods: Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like mouse model was used in this study. Mice were treated with electroacupuncture at DU20 and SP10 (depth of 2-3 mm, frequency of 2/15 Hz, intensity of 0.5-1.0 mA, 10 min/day). The severity of psoriasis-like lesions for each group was assessed. In addition, histological analysis of the lesions were performed. The levels of inflammatory cytokines were determined using Elisa. The expression levels of Substance P (SP) and NK1R were measured using Western blotting. In addition, NK1R inhibitor was administrated to evaluate the target of electroacupuncture in our mouse model.
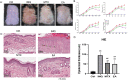
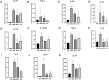
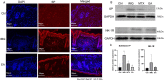
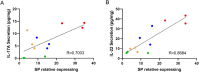
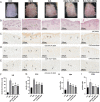
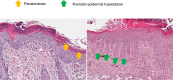
Results: Electroacupuncture significantly alleviated IMQ-induced skin lesions and epidermal thickness, accompanied with reduced keratinocyte proliferation, CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells infiltration. The reduced levels of inflammatory cytokines was observed after electroacupuncture treatment. In addition, electroacupuncture inhibited the expression levels of SP and NK1R. NK1R inhibitor could ameliorate lesional symptoms and suppress epidermal thickening and CD3+, CD4+, and CD8 + T cell infiltration.
Conclusions: Electroacupuncture relieved psoriasis-like inflammation and T cell infiltration. This therapeutic action was likely mediated by the modulation of Substance P and its receptor NK1R.
Keywords: Electroacupuncture; Inflammation; Neurokinin-1 receptor; Psoriasis; Substance P.
© 2023 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acupuncture Needling, Electroacupuncture, and Fire Needling Improve Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions through Reducing Local Inflammatory Responses.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Jul 29;2019:4706865. doi: 10.1155/2019/4706865. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31467575 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of electroacupuncture intervention on angiogenesis in psoriasis mice.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024 Jun 25;49(6):577-584. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20230379. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024. PMID: 38897801 Chinese, English.
-
Effect of γ-secretase inhibitor on Th17 cell differentiation and function of mouse psoriasis-like skin inflammation.J Transl Med. 2018 Mar 10;16(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1442-6. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29523162 Free PMC article.
-
Research on electroacupuncture parameters for knee osteoarthritis based on data mining.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Aug 31;27(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00795-9. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36045455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture: A New Approach for Improved Postoperative Sleep Quality After General Anesthesia.Nat Sci Sleep. 2020 Aug 21;12:583-592. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S261043. eCollection 2020. Nat Sci Sleep. 2020. PMID: 32922103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acupoints for Headache with Blood Stasis Syndrome: a Literature Study Based on Data Mining Technology.J Pain Res. 2024 Jul 26;17:2455-2471. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S471441. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39081327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Michalek I.M., Loring B., John S.M. A systematic review of worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31(2):205–212. - PubMed
-
- Sandoval-Talamantes A.K., Gomez-Gonzalez B.A., Uriarte-Mayorga D.F., et al. Neurotransmitters, neuropeptides and their receptors interact with immune response in healthy and psoriatic skin. Neuropeptides. 2020;79 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
